
免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Blackheads are a common skin concern that many individuals face. These small, dark spots can be frustrating to deal with and may affect your confidence. However, with the right knowledge and proper skincare, you can effectively address blackheads and achieve clearer, healthier-looking skin. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes of blackheads, how to treat them, and essential preventive measures.
1
How Do Blackheads Happen & What are they?
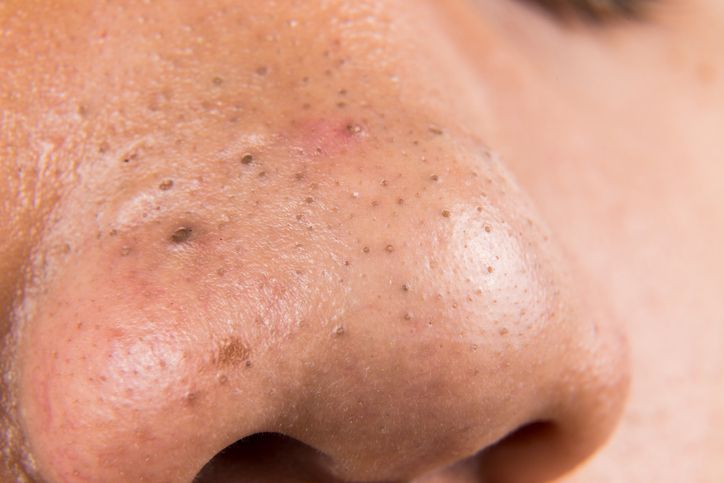
You can say that blackheads are a type of acne characterised by clogged pores. They form when the hair follicles become blocked with excess sebum (oil), dead skin cells, and debris. The clogged pore remains open, allowing air to reach the trapped material, which oxidises and turns black. Contrary to popular belief, the dark colour of blackheads is not due to dirt.
Several factors contribute to the development of blackheads:
1. Excess Sebum Production
Blackheads often form when there is an overproduction of sebum, which is the natural oil produced by the sebaceous glands in the skin. When excess sebum mixes with dead skin cells and other debris, it can clog the hair follicles or pores. This blockage creates an ideal environment for the accumulation of bacteria and the development of blackheads. Some individuals naturally produce more sebum than others, making them more prone to blackhead formation.
2. Dead Skin Cell Buildup
The outermost layer of the skin constantly sheds dead skin cells as a natural part of the skin renewal process. In some cases, these dead skin cells can accumulate on the skin's surface and within the hair follicles. When combined with excess sebum, the dead skin cells can form a plug that obstructs the follicles, leading to the formation of blackheads.
3. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations can play a significant role in the development of blackheads, particularly during puberty. During this time, there is an increase in androgen hormones, such as testosterone, which can stimulate the sebaceous glands to produce more sebum. The excess sebum, along with the accumulation of dead skin cells, can contribute to the formation of blackheads and other types of acne. Hormonal changes during menstruation or pregnancy can also impact sebum production and blackhead occurrence.
4. Use of Certain Skincare Products
Some skincare products, particularly those containing comedogenic ingredients, can worsen blackheads. Comedogenic ingredients have a higher likelihood of clogging pores and causing acne breakouts, including blackheads. It's essential to choose non-comedogenic products, which are formulated to minimise pore blockage and reduce the risk of blackhead formation.
5. Environmental Factors
Environmental factors, such as exposure to pollutants, dirt, and humidity, can contribute to the development of blackheads. Pollutants and dirt on the skin's surface can mix with sebum and dead skin cells, further clogging the pores. Humid environments can lead to excess sweating and sebum production, exacerbating blackhead formation in individuals already prone to it.

2
Prevent and Treat Blackheads with These Methods

1. Maintain a Consistent Skincare Routine with Products Suitable for Your Skin Type
Consistency is key in preventing and treating blackheads. Establish a daily skincare routine that includes cleansing, exfoliating, and moisturising. Choose products that are specifically formulated for your skin type, whether it's oily, dry, combination, or sensitive. A well-suited skincare routine helps maintain the balance of your skin and reduces the likelihood of blackhead formation.
2. Use Gentle Exfoliation to Remove Dead Skin Cells and Unclog Pores
Regular exfoliation is essential in preventing blackheads by removing dead skin cells and unclogging pores. However, avoid harsh scrubbing or abrasive exfoliants that can irritate the skin. Instead, opt for gentle exfoliants with ingredients like alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), such as salicylic acid. These chemical exfoliants work to dissolve the dead skin cells and help prevent pore blockages.
3. Avoid Using Comedogenic Skincare Products
Comedogenic products have a higher likelihood of clogging pores and promoting acne, including blackheads. Check product labels and avoid skincare or makeup products that are labeled as comedogenic. Opt for non-comedogenic or oil-free alternatives to minimise the risk of blackhead formation.
4. Keep the Skin Clean by Washing It Twice Daily with a Mild Cleanser
Regularly cleansing the skin is crucial in removing excess oil, dirt, and impurities that can contribute to blackheads. Wash your face twice daily using a mild, non-drying cleanser. Avoid harsh cleansers that strip the skin of its natural oils, as this can lead to increased sebum production and potential blackhead formation.
5. Use Non-Comedogenic Makeup and Avoid Heavy or Oily Cosmetics
When choosing makeup products, opt for non-comedogenic options that won't clog pores. Avoid heavy or oil-based cosmetics, as they can contribute to pore blockage and worsen blackheads. Look for makeup products labelled as "oil-free" or "non-comedogenic" to reduce the risk of breakouts.
6. Avoid Squeezing or Picking at Blackheads, as This Can Lead to Inflammation and Scarring
It can be tempting to squeeze or pick at blackheads, but this should be avoided. Squeezing can push the contents deeper into the pore or cause trauma to the skin, leading to inflammation and potential scarring. Instead, focus on a consistent skincare routine with gentle exfoliation to help minimise blackheads.
7. Consider Using Topical Treatments with Ingredients like Salicylic Acid or Benzoyl Peroxide, Which Can Help to Reduce Blackheads
Over-the-counter topical treatments containing ingredients like salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide can be effective in treating and preventing blackheads. Salicylic acid helps to exfoliate the skin and unclog pores, while benzoyl peroxide has antibacterial properties that can target acne-causing bacteria. These treatments can help to reduce blackheads and improve overall skin texture.
If you have persistent or severe blackheads:
If you have persistent or severe blackheads that do not improve with over-the-counter treatments, it's best to consult with a dermatologist or skincare professional for personalised advice and treatment options. They can recommend prescription-strength treatments or procedures, such as chemical peels or professional extractions, to effectively manage blackheads and achieve clearer, healthier skin.
By understanding the contributing factors to blackheads and adopting a suitable skincare routine, you can take proactive steps to prevent and treat blackheads, leading to improved skin health and a smoother complexion.
3
Get Rid of Blackheads Takes Too Much Time! What Happens if I Leave Them Alone?

If you leave blackheads alone, they may not necessarily turn into acne, but they can persist and potentially worsen over time. Blackheads are a type of non-inflammatory acne lesion, also known as open comedones. They occur when a hair follicle or pore becomes clogged with excess sebum (skin oil), dead skin cells, and sometimes bacteria. The clogged pore remains open to the air, and its contents oxidise, giving the blackhead its characteristic dark appearance.
Here's what can happen if you leave blackheads untreated:
1. Persistence
Blackheads can remain on the skin for an extended period if left untreated. They may not cause significant harm or discomfort on their own, but they can be unsightly and affect the appearance of your skin.
2. Worsening
While blackheads are non-inflammatory and generally not painful, they can worsen over time if the underlying causes are not addressed. Without proper skincare and prevention, more blackheads may develop, and the existing ones can become larger or more widespread.
3. Potential for Enlarged Pores
Prolonged presence of blackheads can stretch the pores, making them appear larger. Enlarged pores are more susceptible to becoming clogged, leading to a cycle of continued blackhead formation.
4. Risk of Inflammation
Although blackheads themselves are non-inflammatory, if bacteria become trapped within the clogged pore, it can lead to inflammation and the development of inflammatory acne lesions such as papules, pustules, or nodules. This transition from non-inflammatory to inflammatory acne can occur if blackheads are picked, squeezed, or manipulated, introducing bacteria into the skin.
5. Secondary Infections
Manipulating blackheads or trying to squeeze them can lead to skin trauma, which may create openings for bacteria to enter and cause infections. This can result in more severe acne breakouts and potential scarring.

4
Eventually, they will be your enemy to a smoother skin.

In worse cases, blackheads can turn into acne, specifically inflammatory acne, in certain cases. Inflammatory acne refers to acne lesions that involve redness, swelling, and sometimes pain due to inflammation. While blackheads themselves are non-inflammatory, the following factors can contribute to their transformation into inflammatory acne:
1. Bacterial Infection
Blackheads are caused by the clogging of pores with excess sebum, dead skin cells, and other debris. If bacteria, such as Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), become trapped within the clogged pore, they can multiply and cause an inflammatory response. This leads to the development of inflammatory acne lesions, such as papules, pustules, and nodules.
2. Skin Irritation
Picking, squeezing, or otherwise manipulating blackheads can cause skin irritation and trauma. This can damage the pore's lining and introduce bacteria into the surrounding skin, leading to inflammation and the formation of inflammatory acne.
3. Excessive Oil Production
If the skin continues to produce excessive sebum, it can contribute to more clogged pores and the potential for bacterial overgrowth. This excess oil production is often influenced by hormonal factors, genetics, and certain lifestyle habits.
4. Environmental Factors
Factors such as pollution, humidity, and dirt can exacerbate blackheads and contribute to bacterial growth on the skin. These external factors can increase the likelihood of blackheads turning into inflammatory acne.
5. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during puberty, menstruation, or pregnancy, can increase sebum production. Higher sebum levels can lead to more blackheads, and if bacterial infection occurs, it can progress to inflammatory acne.
6. Diet and Lifestyle
Certain dietary and lifestyle habits, such as consuming a high-glycemic diet, smoking, or experiencing chronic stress, can impact skin health and influence the development of acne.
To prevent blackheads from turning into inflammatory acne, it's crucial to practice good skincare habits and avoid picking or squeezing blackheads. Maintaining a consistent skincare routine, using non-comedogenic products, and avoiding excessive oil buildup can help manage blackheads and reduce the risk of inflammation.

免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
5
Recommended Skincare Routine for Blackheads and Acne Prone Skin

For individuals prone to blackheads, a simple yet effective skincare routine can play a significant role in preventing and managing blackheads. Here's a detailed elaboration of the morning and evening skincare routine:
Morning Routine
1. Cleanse with a Gentle, Oil-Free Cleanser: Start your morning routine by cleansing your face with a gentle, oil-free cleanser. Look for a cleanser that is specifically formulated for your skin type and is non-comedogenic. Gently massage the cleanser onto damp skin, then rinse thoroughly with lukewarm water. This step helps remove any excess oil, sweat, and impurities that may have accumulated on your skin overnight.
2. Apply a Lightweight, Non-Comedogenic Moisturiser: After cleansing, follow up with a lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturiser. Even if you have oily skin, it's essential to use a moisturiser to keep your skin hydrated and balanced. Look for a moisturiser that is oil-free and won't clog pores. Proper hydration can help maintain a healthy skin barrier and reduce the risk of excess oil production that can contribute to blackheads.
3. Follow with a Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen: Sunscreen is a crucial step in any skincare routine, even if you have blackhead-prone skin. Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 to protect your skin from harmful UV rays. Sunscreen helps prevent sun damage and premature ageing, and it also reduces the risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, which can occur after resolving acne lesions.
Evening Routine
1. Double Cleanse to Thoroughly Remove Makeup and Impurities: In the evening, start with a double cleanse to thoroughly remove makeup, sunscreen, and any accumulated dirt or pollutants from the day. First, use an oil-based cleanser or micellar water to dissolve and lift makeup and sunscreen. Follow up with a water-based cleanser to cleanse the skin thoroughly. Double cleansing ensures a clean canvas for the following steps and helps prevent pore blockages.
2. Exfoliate 1-2 Times a Week: Exfoliation is an essential step in managing blackheads. One to two times a week, use a gentle exfoliant containing alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs) or beta hydroxy acids (BHAs), such as salicylic acid. Exfoliation helps remove dead skin cells and unclog pores, preventing the formation of blackheads and promoting smoother skin texture.
3. Apply a Retinoid Cream or Serum: Retinoids are vitamin A derivatives known for their effectiveness in treating and preventing acne. Apply a retinoid cream or serum as part of your evening routine. Retinoids work by increasing cell turnover, reducing clogged pores, and promoting a healthier complexion. Start with a lower concentration and gradually increase usage to avoid irritation.
4. Moisturise as Needed: After applying the retinoid, moisturise your skin as needed. Some individuals may experience dryness or irritation from retinoids, so it's essential to keep the skin hydrated. Choose a moisturiser that suits your skin type and is compatible with the retinoid you're using. Applying a moisturiser can also help mitigate potential irritation from the exfoliation step.
By following this comprehensive skincare routine, individuals prone to blackheads can effectively manage their skin's health, minimise pore blockages, and reduce the occurrence of blackheads. Remember that consistency is key, and it's essential to use products suitable for your skin type and concerns. If you have specific skincare concerns or persistent blackhead issues, you might need further help from a skincare professional for personalised advice and treatment recommendations, and here's where Perfect Medical can help!

6
Treat Acne and Blackheads with Perfect Medical's Acne Treatment

This treatment is specifically designed to address the concerns of oily, acne-prone skin, aiming to improve various skin issues like pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, enlarged pores, dry skin, acne scars, and a lacklustre appearance. The process involves a twin spiral suction and drainage system that effectively removes excess oil and dead skin cells, preventing further pore clogging.
To soothe acne-prone skin, a medical-grade moisturising serum is incorporated into the treatment. This serum penetrates deeply into the skin, providing essential hydration and nourishment. As a result, inflammation is reduced, and the overactive oil-producing sebaceous glands are calmed.
One of the notable benefits of this treatment is that it is non-invasive, meaning there are no surgeries, incisions, injections, topical antibiotic creams, or oral antibiotics required. Over time, with consistent treatment, pimples, scars, and other acne manifestations can significantly improve, leading to a healthier and more radiant complexion!
- How Does Pimple Patch Improve Acne and Breakout? What Are the 10 Best Pimple Patches?
- Back Acne: Why Are They So Irritating? Find Out What You Can Do To Get Rid Of Them
- Tackle Adult Acne With Confidence: Know What Are They And How To Treat Them
- Prepare Your Own Acne Scarring Home Remedies Couldn't Be Easier! Here's 3 Ways To Make Them
7
Conclusion
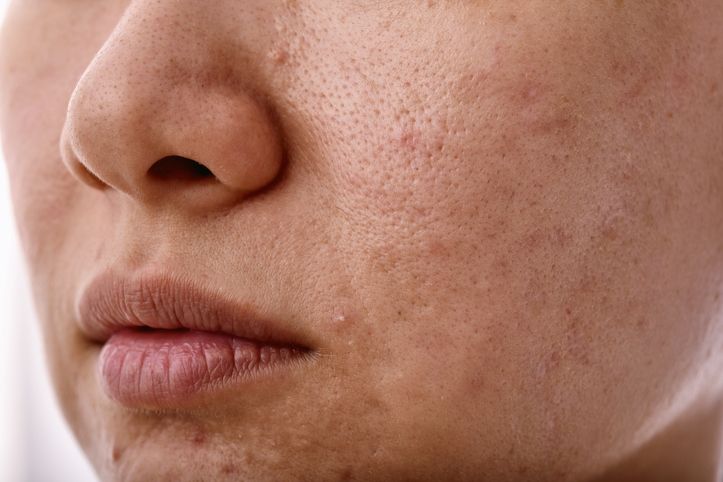
By opting for Perfect Medical's assistance, you can effectively reduce the appearance of blackheads and enjoy healthier, plump, and less oily skin. However, it's essential to exercise caution and avoid overdoing it within a very short period of time, as excessive treatment can potentially cause adverse effects such as skin rashes or peeling, or even results in sensitive skin. Consistency and moderation are key to achieving the best results without causing harm to your delicate skin barrier.

免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

1. Are blackheads the same as whiteheads?
No, blackheads and whiteheads are different types of acne. Blackheads are open comedones, while whiteheads are closed comedones.
2. Can squeezing blackheads make them worse?
Yes, squeezing blackheads can push the contents deeper into the skin, leading to inflammation and potential scarring.
3. Can diet impact blackhead formation?
Some studies suggest that a high-glycemic diet may exacerbate acne, but more research is needed.
4. Can blackheads turn into pimples?
If the blackhead becomes inflamed and infected, it can turn into a pimple or acne lesion.
5. Are blackheads only a teenage skin concern?
No, blackheads can affect individuals of all ages, although they are more common during puberty.





