- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets

免費體驗
Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Do you or your loved one snore a lot? If you've ever wondered about the reasons behind this common phenomenon and how to put an end to the disruptive noise, you're in the right place. Snoring can be more than just a nighttime annoyance – it might also be an indication of underlying health issues. This article delves into the world of snoring, shedding light on its causes, potential risks, and effective remedies to help you or your partner enjoy quieter nights.
1
Why Do I Often Have Snoring Issues and Disrupted Sleep?

Snoring, that characteristic cacophony of sound during slumber, arises when the flow of air is obstructed partially during sleep. This sonic disturbance originates from the vibration of soft tissues within the throat and nasal passages, which tend to relax during periods of rest. A comprehensive understanding of snoring necessitates an exploration of the multifaceted factors contributing to its occurrence, a perspective informed by both empirical observations and scientific research.
Obstructed airways
Snoring often originates from partially blocked airways that are responsible for carrying air during breathing. This blockage can be caused by factors like relaxed throat muscles or congested nasal passages, which hinder smooth airflow. The combination of how our bodies are built and the relaxation of muscles forms the basis of snoring.
Sleep position
How we sleep also plays a significant role in snoring. Sleeping on our back can lead the tongue and soft palate to collapse toward the back of the throat. This shift disrupts the normal path of airflow, resulting in the sound of snoring. Studies, like one published in the Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, show a connection between sleep position and the intensity of snoring.
Age and weight
As we age, our throat muscles tend to lose their tone, making snoring more likely. Additionally, body weight has an impact. Research from the "International Journal of Obesity" explains how weight gain can lead to increased snoring due to specific mechanisms.
Alcohol and sedatives
Consuming alcohol or sedatives causes muscles, including those in the throat, to relax. This relaxation narrows the airway, making snoring more probable.
Nasal issues
The nasal passages are crucial for smooth airflow, but issues like congestion or structural problems can disrupt this flow. These obstacles create an environment conducive to snoring. Research in the "American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy" delves into how nasal conditions affect snoring, giving us a better understanding of this interaction.
In summary, snoring is a complex sound that arises from a mix of factors involving anatomy, physiology, and lifestyle. While often harmless, snoring can also point to underlying health issues. Understanding these factors can lead to interventions that improve sleep quality and overall well-being.
2
2 Fun Facts About Snoring That You Might Not Know

1. Men Snores More Than Women
Research consistently indicates that there is a notable gender difference when it comes to snoring frequency. Generally, snoring is more prevalent in men than in women. Studies have shown that approximately 40% of adult men are regular snorers, while around 24% of adult women snore regularly. This discrepancy in snoring rates between men and women can be attributed to a combination of anatomical, physiological, and hormonal factors.
Anatomically, men tend to have narrower airways than women, which can contribute to increased turbulence in airflow during breathing, leading to a higher likelihood of snoring. Additionally, hormonal influences, such as testosterone, can affect muscle tone in the throat and airway, potentially contributing to snoring in men.
It's important to emphasise that while snoring is more prevalent in men, it can still occur in women, and the severity and frequency of snoring can vary widely among individuals of both genders. The underlying causes of snoring can also be multifaceted and may include factors such as obesity, sleep position, nasal congestion, and lifestyle habits.
In summary, research consistently supports the observation that a larger percentage of men tend to snore regularly compared to women. However, snoring is a complex phenomenon influenced by various factors, and its occurrence can vary within both genders.
2. Overweight people snore more often
There is a noticeable association between being overweight and an increased propensity to snore. The mechanics behind this connection lie in the intricate interplay of anatomy, physiology, and sleep quality. Let's delve deeper into the reasons why overweight individuals are more prone to snoring.
Snoring occurs when the flow of air through the mouth and nose is partially obstructed during sleep. This obstruction leads to the surrounding tissues vibrating, creating the characteristic snoring sound. One of the key contributors to snoring is the relaxation of the muscles in the throat and the narrowing of the airway passage. Excessive body weight, especially concentrated around the neck and throat area, can exacerbate this narrowing of the airway.
When a person gains weight, particularly in the form of adipose tissue (fat), it can accumulate in various parts of the body, including the neck. This additional tissue can put pressure on the internal structures of the throat, causing the airway to become narrower. As a result, during sleep, the passage of air through the narrowed airway encounters resistance, leading to turbulent airflow and vibrations that manifest as snoring.
Furthermore, excess weight can lead to a decrease in muscle tone in the throat area. Muscles that help keep the airway open might become lax due to the extra weight, contributing to further airway collapse during sleep. This is especially relevant during deep sleep when muscle tone naturally decreases, making the airway even more susceptible to collapse.
- 4 Types Of People Should Avoid Anti-Snoring Devices + 5 Daily Habits To Improve Snoring! Editor’s Review Of The Popular “Snoring Gun”
- Proper Use of Nasal Washers for Nasal Irrigation + Choosing Nasal Washers and Saline
- Shortness of Breath at Night: Causes, Treatments, and When to Seek Help
- The Truth Behind Snoring! Do Anti-Snoring Mouthguards Really Work? Try the Painless Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment!
3
The Health Implications of Excessive Snoring
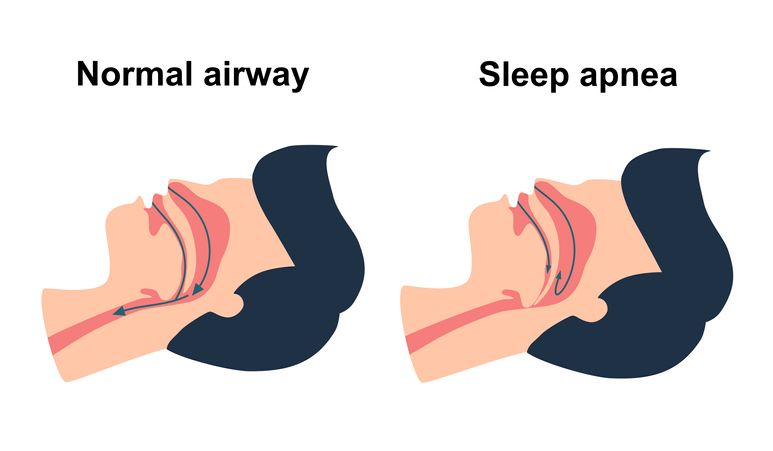
Snoring, a common occurrence, can unveil important health issues that deserve careful attention. Beyond the sound of snoring lies a world of physiological intricacies that might point to underlying problems. Chronic snoring, in particular, can be a sign of health concerns that go beyond mere noise.
Sleep apnea
Chronic snoring can signal a sleep disorder called sleep apnea. This condition causes repeated pauses in breathing during sleep, disrupting the natural sleep cycle and leading to fragmented rest. Studies in the "Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine" highlight the link between snoring and sleep apnea, showing how it can affect overall health.
Cardiovascular conundrums
Persistent snoring is more than just an annoyance – it's connected to cardiovascular health. Research published in "Circulation" reveals that chronic snoring is linked to a higher risk of hypertension and other heart issues. Snoring might indicate potential cardiovascular concerns that need attention.
Daytime fatigue
Snoring's nighttime noise often leads to daytime exhaustion. Poor sleep quality due to chronic snoring can result in daytime fatigue, leading to excessive sleepiness and reduced alertness during the day, or even lead to serious sleep disorder in the long run.
Strains on relationships
The effects of snoring can impact relationships as well. Partners of chronic snorers might also experience sleep disturbances.
In essence, snoring isn't just about the noise – it's a complex story that goes beyond sound. Chronic snoring acts as a signal, urging individuals to consider their overall health. Recognizing the potential links to sleep apnea, cardiovascular problems, daytime fatigue, and relationship dynamics empowers individuals to take steps that align sleep with well-being.
4
Lifestyle Changes You Can Try to Soothe Snoring Woes

Change sleep position
If snoring is an issue, trying a different sleeping position can be helpful. Sleeping on your side, instead of your back, can prevent the collapse of throat tissues that contribute to snoring. This change encourages smoother airflow and can lead to quieter nights. Research published in the "Journal of Sleep Research" explains the benefits of sleeping on your side and how it can reduce snoring.
Maintain a healthy weight
Working towards a healthier weight can make a significant impact on snoring. Losing excess weight reduces the pressure on your airways, allowing for better airflow during sleep. Studies in the "American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine" confirm that weight loss can lead to a decrease in snoring frequency and intensity.
Elevate your head when sleeping
Adjusting the angle of your head while sleeping can be effective in reducing snoring. You can achieve this by using an extra pillow or by slightly elevating the head of your bed. This slight elevation can help keep your airways open and promote smoother breathing. Research in the "European Respiratory Journal" supports this method as a way to alleviate snoring.
Stay hydrated
Staying well-hydrated has benefits beyond quenching your thirst – it can also help reduce snoring. Proper hydration prevents the buildup of sticky secretions in your nasal passages, which can contribute to snoring. By drinking enough water throughout the day, you're promoting clear airflow and potentially quieter sleep.
Limit alcohol and sedatives
What you consume before bedtime matters. Alcohol and sedatives relax muscles in your body, including those in your throat. This relaxation can increase the likelihood of snoring. By avoiding these substances in the hours leading up to sleep, you can help prevent muscle relaxation and potential snoring.
Nasal strips or dilators
Nasal strips or dilators are simple devices that can improve the airflow through your nasal passages. They gently open up your nostrils, making it easier to breathe through your nose while you sleep. These devices have been shown to be effective in reducing snoring disruptions during the night, as indicated by studies in the "Sleep and Breathing" journal.
Medical interventions
If snoring becomes a significant issue, there are medical interventions to consider. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy involves wearing a mask that delivers a gentle stream of air to keep your airways open. Surgical procedures can also be an option in more severe cases. "Chest" provides valuable insights into the options available and how they can address persistent snoring.
To sum up, addressing snoring involves a range of approaches that can contribute to better sleep quality for both you and your bed partner. By trying different strategies like adjusting sleep position, maintaining a healthy weight, elevating your head, staying hydrated, limiting certain substances, using devices, or considering medical interventions, you have the potential to enjoy quieter and more restful nights.

免費體驗
Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
5
Stop Snoring in No Time with Perfect Medical's Help

Restful nights of sleep are now attainable for those dealing with sleep apnea, thanks to the revolutionary Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment offered by Perfect Medical. This innovative laser-based approach brings hope by improving sleep quality and overall well-being without invasive methods. Using laser technology, this treatment offers a gentle yet effective solution for sleep apnea and snoring.
At the core of this treatment is the use of laser energy to delicately tighten oral tissues. The laser prompts collagen in the mouth's mucosa tissue to subtly contract, reducing the slackness that contributes to sleep apnea and snoring. The precision of the treatment is highlighted by its controlled and secure application of laser waves to the targeted area, ensuring optimal results with minimal risk.
What sets the Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment apart is its efficiency and quick effects. There's virtually no recovery time, allowing individuals to experience swift improvements in sleep quality. A brief sensation of throat dryness, easily managed with hydration before and after treatment, is the only temporary side effect. It's important to note that addressing sleep apnea might require multiple sessions for maximum effectiveness.
Dealing with sleep apnea doesn't have to be daunting. Taking the proactive step of scheduling an appointment can lead to revitalised sleep and improved well-being. The Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment offers a transformative solution, inviting individuals to embrace better sleep, health, and vitality. Choose to embark on a journey toward renewed sleep and energy today.
Additional benefits of this treatment
- Revitalise Sleep Quality: This treatment revolutionises sleep quality, granting individuals the respite they deserve from the clutches of sleep apnea and snoring.
- Non-Invasive Solution: Perfectly balancing efficacy and comfort, this laser-based approach requires no invasive procedures, prioritising safety and minimal discomfort.
- Swift Results, Lasting Impact: With rapid effects and no extended recovery, individuals can swiftly experience the benefits of improved sleep while setting the stage for lasting well-being.
- Customised Treatment: The treatment's controlled and adaptable nature ensures that each session is tailored to the individual's unique needs, ensuring maximum effectiveness.
- Professional Expertise: Administered by experts at Perfect Medical, this treatment assures precision and expertise in delivering its transformative effects.
6
Last Few Words

Living with someone who snores a lot or dealing with excessive snoring yourself can be challenging. However, with the right understanding and proactive steps, you can mitigate its impact on your sleep quality and overall well-being. From lifestyle adjustments to medical interventions, there are solutions that can help you enjoy quieter nights and wake up refreshed. The journey to silence the nocturnal symphony of snoring navigates a landscape rich in strategies. The selection of these harmonising techniques weaves a narrative of empowerment and underscores the multifaceted symphony of sleep.
So, whether it's implementing simple changes or seeking medical advice, remember that relief from excessive snoring is within reach. By addressing the root causes and exploring suitable remedies, you're paving the way for restful nights and revitalised days.

免費體驗
Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

1. Is snoring usually caused by obstructive sleep apnea?
A: It is commonly understood that snoring can be associated with obstructive sleep apnea in certain cases. Obstructive sleep apnea occurs when the airway is partially or completely blocked during sleep, leading to interruptions in breathing and potentially causing snoring as a symptom.
2. Can a deviated septum cause excessive snoring?
A: Yes, a deviated septum, which is the displacement of the wall between the nostrils, can contribute to excessive snoring. The uneven structure of the septum can obstruct airflow through the nose, leading to increased snoring.
3. Are over-the-counter devices effective?
A: Over-the-counter devices such as nasal strips can provide relief for some individuals by helping to open nasal passages and improve airflow. However, the effectiveness of these devices can vary from person to person, and they may not be a suitable solution for everyone.
4. Can children snore?
A: Yes, children can snore for various reasons. Common causes include allergies, colds, or enlarged tonsils or adenoids. If you're concerned about your child's snoring, it's recommended to consult a paediatrician. They can assess the situation and provide guidance on whether further evaluation or treatment is needed.
5. How do throat muscles function during snoring?
A: During snoring, the muscles in the throat, including the soft palate and the uvula, can become relaxed and partially block the airway. As you breathe, the flow of air causes these relaxed tissues to vibrate, producing the sound we recognize as snoring. The muscles in the throat normally help to keep the airway open and unobstructed. However, factors like sleeping position, alcohol consumption, obesity, and certain sleep disorders can contribute to the relaxation of these muscles, leading to snoring. In more severe cases, this relaxation can even cause obstructive sleep apnea, where the airway becomes completely blocked, briefly interrupting breathing and affecting overall sleep quality.