- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets

免費體驗
Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Snoring, a nightly symphony for many, might seem harmless, but it could signal more significant health issues, particularly obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). For those who are not sure what mouth snoring can bring, read on to discover the potential health implications and why addressing this seemingly innocuous habit is essential for your overall well-being.
1
What Exactly is Obstructive Sleep Apnea?

OSA occurs when the soft palate and throat tissues relax too much during sleep, creating a potential blockage in the upper airway and causing breathing interruptions. One telltale sign of OSA is loud snoring, often accompanied by moments of paused breathing during sleep. The key players in this scenario are the tongue and throat muscles, essential for maintaining an open airway. When these muscles relax excessively, snoring and disruptive sleep patterns emerge, leading to problems like daytime fatigue, morning headaches, and overall poor sleep quality.
2
How Do I Know If I Have Sleep Apnea?

If you're unsure whether you snore through your mouth, consider the following indicators:
Observation by Others
If those who share a sleeping space with you have observed and mentioned your snoring habits, especially if they note that you often snore with your mouth open, this feedback is a valuable indicator of mouth snoring. Often, others may be more aware of your sleep behaviours, and their observations can prompt further investigation into potential snoring issues.
Dry Mouth and Throat
Mouth snoring can lead to the habit of breathing through the mouth during sleep, which may result in waking up with a dry mouth and throat. This occurs because breathing through the mouth can reduce saliva production. If you consistently experience dryness or soreness in your mouth and throat upon waking, it is suggestive of mouth snoring as a potential cause.
Morning Symptoms
Paying attention to any symptoms experienced in the morning can offer clues about your sleep patterns. If you frequently wake up with a dry or sore throat, it could be an indication that you are breathing through your mouth during the night. Morning symptoms can serve as personal indicators that prompt further investigation into potential snoring issues.
Sleep Disruptions
Mouth snoring may contribute to sleep disruptions, affecting both your own sleep quality and that of anyone sharing your sleeping space. If you often wake up feeling tired, unrested, or experience sleep deprivation, it may be worthwhile to explore whether snoring, particularly through the mouth, is a contributing factor to these disruptions.
Sleep Partner Feedback
If you have a sleep partner, their feedback can be instrumental in understanding your snoring habits. Asking them about your snoring patterns, especially whether you predominantly snore through your mouth, provides external observations that can contribute to a comprehensive understanding of your sleep behaviour.
Personal Awareness
Individuals may sometimes be personally aware of their snoring patterns. If you notice that you tend to breathe through your mouth during sleep, particularly when snoring is present, it serves as a direct personal awareness indicator of mouth snoring. This self-awareness can be a crucial step in addressing and exploring potential solutions for snoring-related concerns.
- Snoring Relief Guide: 5 Proven Methods + 6 Highly Recommended Devices! Practical Tips for Different Snoring Levels
- Expert Breakdown on Snore Guns Mechanism, Effectiveness, and Side Effects
- Do Snoring Chin Straps and Mouthpieces Really Work? Smart Solution or Just a Gimmick?
- Does the Snore Gun Really Work? The Guide to Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment — Mechanism, Effectiveness & Side Effects Explained
3
The Question Arises: Can Mouth Snoring Be Life-Threatening?

To answer, we must recognize the potential risks associated with what might seem like a harmless habit. The consequences of disrupted sleep extend beyond the audible annoyance of snoring.
This obstruction can result in decreased oxygen levels in the blood, putting strain on the heart and other organs. Over time, untreated sleep apnea can increase the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
In severe cases, when someone experiences sleep apnea, their breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. This interruption in breathing can lead to a dangerous decrease in the levels of oxygen in the bloodstream. The lack of oxygen puts strain on the body, particularly the heart, and can result in serious health complications.
One significant risk associated with severe sleep apnea is the development of arrhythmias, which are irregular heartbeats. The inconsistent flow of oxygen to the heart can disrupt its normal rhythm, potentially leading to palpitations and other heart-related issues. Over time, untreated sleep apnea can contribute to the progression of cardiovascular problems, including high blood pressure, heart disease, and an increased likelihood of experiencing a stroke.
In the most extreme situations, severe sleep apnea can even be life-threatening, as the repeated pauses in breathing may lead to sudden cardiac arrest. Sudden cardiac arrest occurs when the heart abruptly stops beating, and it requires immediate medical intervention, such as cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and emergency medical assistance.
4
Wonder Why You Can't Stop Snoring? These Could Be the Reasons

Occasional instances of mouth snoring may not be an immediate cause for concern, but persistent and loud snoring should not be overlooked. Understanding the factors associated with snoring and obstructive sleep apnea is crucial, as it can help identify potential underlying issues. Several factors contribute to the development and worsening of snoring, including sleep position, weight, and lifestyle choices.
Sleeping on your back
Sleeping in this position can worsen snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. When lying on the back, the throat tends to narrow, and the tongue may slide backward, causing a more significant obstruction in the airway. Changing sleep positions, such as sleeping on your side, may help alleviate this issue.
Excess weight
Having excess weight, especially around the neck and throat area, can contribute to snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. The additional weight can put pressure on the airway, making it more prone to collapse or partial blockage during sleep. Weight loss through a healthy diet and regular exercise can be beneficial in reducing snoring in such cases.
Poor muscle tone
Weakness or poor tone in the muscles of the throat and tongue can contribute to snoring. When these muscles are not adequately toned, they are more likely to collapse and obstruct the airway during sleep. Incorporating exercises that target throat and tongue muscles, as well as overall fitness routines, can help improve muscle tone and reduce snoring.
Enlarged tonsils or adenoids
In some cases, snoring may be linked to enlarged tonsils or adenoids, especially in children. These structures, located at the back of the throat, can contribute to the narrowing of the upper airway. Medical evaluation, particularly for children, can determine if enlarged tonsils or adenoids are a contributing factor to snoring, and appropriate treatment options can be explored.

免費體驗
Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
5
9 Ways To Stop Snoring Every Night: Do They Work?

There are various approaches to address snoring and obstructive sleep apnea, ranging from non-invasive methods to medical interventions.
Non-Invasive Methods
- Anti-Snoring Pillows Anti-snoring pillows are designed to support proper head and neck alignment, helping to keep the airways open. They aim to reduce snoring by preventing the throat from collapsing during sleep, promoting better airflow and minimising the chances of obstruction.
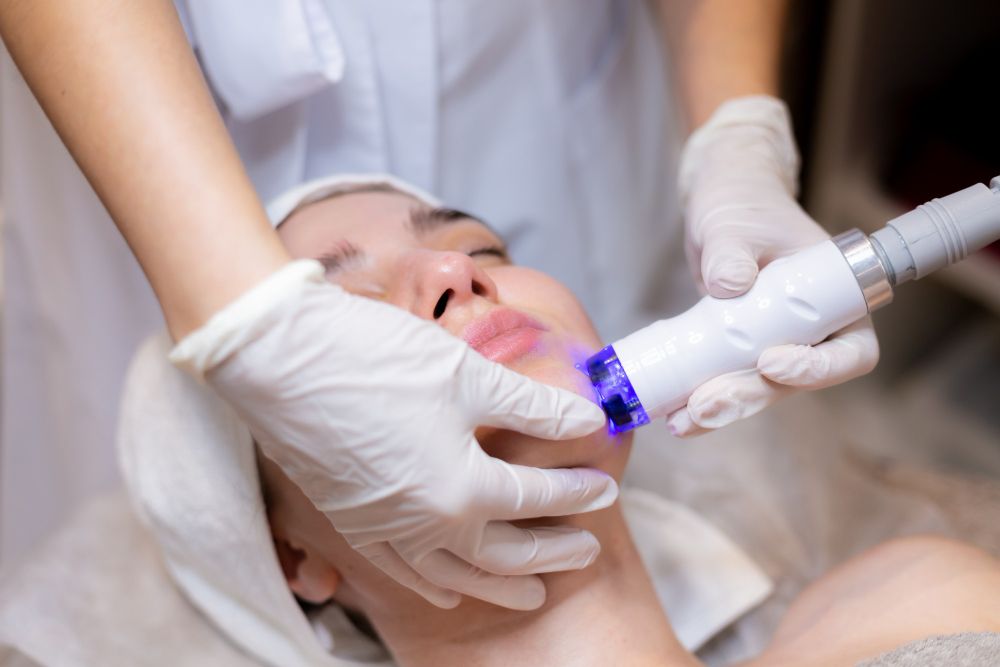
- Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment This treatment is an effective and innovative approach to address snoring without resorting to invasive or surgical procedures. This non-invasive and painless treatment utilises NightLase Laser Technology to specifically target and tighten the collagen fibrous networks present in the tissues of the mouth. The process involves directing the laser towards these collagen fibres, inducing a tightening effect that leads to the contraction and reduction in size of the soft tissues within the mouth. This reduction in tissue size is crucial as it opens up the airway, directly addressing the root cause of snoring.
- Nasal Strips Nasal strips are adhesive strips placed on the outside of the nose. They work by physically widening the nostrils, which can enhance nasal breathing and reduce snoring. Nasal strips are a non-intrusive solution that may provide relief for individuals with nasal congestion issues.
Medical Devices
- Mouth Guards Dental devices or mouth guards are designed to reposition the lower jaw and keep the mouth closed during sleep. By adjusting the jaw position, these devices aim to prevent the collapse of the airway, reducing snoring and, in some cases, addressing mild obstructive sleep apnea.
Surgical Interventions
- Correction of Deviated Septum Surgical procedures may be considered to correct a deviated septum, a condition where the nasal septum is off-centre, potentially obstructing airflow. Septoplasty is a surgical option to straighten the septum and improve nasal breathing.
- Tissue Removal from the Throat For severe cases, surgical interventions may involve removing excess tissue from the throat. Procedures such as uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) aim to address anatomical factors contributing to snoring and obstructive sleep apnea.
It's essential for individuals experiencing persistent snoring or suspected sleep apnea to consult with a healthcare professional. The most suitable approach may vary depending on the underlying causes and severity of the condition.
6
Try These Lifestyle Changes at the Same Time To Prevent Snoring Further

Throat Exercises
Specific exercises targeting throat muscles can help improve muscle tone and reduce the likelihood of airway collapse during sleep. These exercises are designed to strengthen the muscles involved in breathing and swallowing, potentially alleviating snoring.
Weight Loss
Excess weight, especially around the neck and throat, can contribute to airway narrowing and increase the likelihood of snoring. Adopting a healthy diet and regular exercise to achieve weight loss can alleviate pressure on the airway, reducing the occurrence of snoring.
Avoiding Alcohol
Alcohol relaxes muscles, including those in the throat, which can lead to increased snoring. Avoiding alcohol close to bedtime is a lifestyle modification that may help improve sleep quality and minimise snoring.
Sleep Position Adjustment
Changing sleep positions, particularly avoiding sleeping on the back, can be an effective lifestyle change to reduce snoring. Sleeping on one's side helps keep the airway open and minimises throat obstruction.
Hydration
Staying adequately hydrated is essential for overall health and can also help reduce snoring. Proper hydration keeps the throat from becoming sticky and reduces the chances of snoring caused by excess mucus.
Allergen Control
Reducing exposure to allergens in the bedroom, such as dust mites and pet dander, can help alleviate nasal congestion and decrease the likelihood of snoring. Regular cleaning, using hypoallergenic bedding, and maintaining good indoor air quality contribute to this lifestyle change.
7
Conclusion

Addressing snoring and obstructive sleep apnea involves a comprehensive approach that considers various factors, including lifestyle changes, positional therapy, and, if necessary, medical interventions. Seeking the right method and adopting a tailored strategy can significantly contribute to resolving snoring issues and prevent yourself from heading towards a possible life-threatening snoring stage, so be sure to start taking action to let yourself and your partner a good night's sleep.

免費體驗
Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

1. What are some common sleep disorders, and how do they affect overall health?
Sleep disorders encompass a variety of conditions that can significantly impact one's ability to attain restful and rejuvenating sleep. Conditions such as insomnia, sleep apnea, restless legs syndrome, and narcolepsy fall under this category. The effects of sleep disorders extend beyond mere fatigue, potentially leading to issues such as impaired cognitive function, mood disturbances, and an increased risk of chronic health conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Seeking professional help for diagnosis and appropriate management is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
2. Can certain sleep postures contribute to increased snoring, and are there recommended sleeping positions to reduce snoring?
Yes, sleep posture can influence snoring. Sleeping on the back may cause the tongue and soft palate to collapse to the back of the throat, leading to snoring. Sleeping on one's side is often recommended to prevent this collapse and promote optimal airflow. Additionally, using supportive pillows to elevate the head slightly can help reduce snoring. Experimenting with different sleeping positions and pillow configurations may aid in finding the most effective and comfortable solution for minimising snoring.
3. Are there effective exercises to stop snoring, and how can simple mouth and nose exercises help reduce snoring and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA)?
Engaging in mouth and nose exercises can contribute to reducing snoring and symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea. These exercises often focus on strengthening the muscles in the throat and improving overall muscle tone. Techniques such as tongue exercises, throat exercises, and breathing exercises may be beneficial. However, it's essential to note that individual responses to these exercises vary, and consulting with a healthcare professional can provide personalised guidance on their effectiveness.
4. Can surgery, particularly neck surgery, be a solution to resolve snoring, and what are the considerations before opting for such procedures?
Neck surgery, such as uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) or genioglossus advancement (GA), may be considered in certain cases to address anatomical factors contributing to snoring or sleep apnea. However, surgery is typically reserved for severe cases when other interventions have not been effective. Considerations before opting for neck surgery include the severity of the condition, potential risks, and the need for a thorough evaluation by a sleep specialist or an otolaryngologist.
5. How can sleep medicine play a role in managing and eliminating snoring, and what are some commonly prescribed treatments for snoring?
Sleep medicine offers various treatments to manage and, in some cases, eliminate snoring. Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) therapy is a common approach, involving the use of a machine to deliver a steady stream of air to keep airways open. Oral appliances, designed to reposition the jaw and tongue, are another option. Lifestyle changes, weight management, and positional therapy may also be recommended. Consulting with a sleep medicine specialist can help determine the most suitable treatment based on the individual's specific condition and needs.