- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets
Do you or your partner face this nightly struggle that affects millions? Beyond disrupting sleep, snoring can signal underlying health issues. Before you resign yourself to a lifetime of white noise machines, let’s explore the truth behind 9 snoring solutions. In this blog, we’ll distinguish between science-backed remedies and sleep-stealing myths, helping you find the path to a quieter, healthier night’s rest.
Snoring is Caused By What?

To effectively address snoring, it’s crucial to understand its causes. Snoring occurs when the flow of air through the mouth and nose is partially obstructed during sleep, causing the surrounding tissues to vibrate. Key factors contributing to snoring include:
1. Anatomy of the Airway
The physical structure of your throat and nasal passages can play a significant role in snoring. Narrower airways, larger tonsils, or an elongated uvula can make it easier for these passages to become obstructed during sleep, leading to the characteristic sound of snoring.
2. Throat Muscle Tone
During sleep, especially deep sleep, the muscles in your throat relax. If these muscles are overly relaxed, they can collapse inward and partially block the airway. This obstruction disrupts the smooth flow of air and causes the tissues to vibrate, producing the snoring sound. People with naturally lower muscle tone in the throat or who are experiencing extreme fatigue are more prone to this issue.
3. Soft Palate and Uvula
The soft palate, which is the fleshy part at the back of the roof of your mouth, and the uvula, the dangling bit at the back of your throat, can vibrate when air passes over them. If these tissues are larger or thicker, the vibrations are more likely to be louder and more disruptive, contributing significantly to snoring.
4. Nasal Problems
Conditions such as a deviated septum, where the nasal septum (the bone and cartilage dividing the nasal cavity) is off-centre, can lead to chronic nasal congestion. Other nasal issues like allergies or sinus infections can also block the nasal passages. When your nose is blocked, you are more likely to breathe through your mouth, which increases the likelihood of snoring since it changes the airflow and causes more vibrations in the throat.
5. Sleeping Position
Your sleeping position can greatly influence snoring. Lying on your back causes the tongue and soft tissues in your throat to fall backward due to gravity, which can obstruct the airway and lead to snoring. Side sleeping, on the other hand, helps keep the airway open by preventing these tissues from collapsing backward, reducing the chances of snoring.
6. Weight Issue
People with a Body Mass Index (BMI) greater than 25 are more likely to snore. This risk increases as the BMI increases further. Here's a breakdown:
• Overweight (BMI 25-29.9): Increased risk compared to those with a healthy weight (BMI 18.5-24.9).
• Obesity (BMI 30 or higher): Significantly higher risk of snoring and sleep apnea, a more serious condition.
The reason for this is that excess weight, particularly around the neck, can deposit fat tissue that narrows the airway. This narrowing makes it harder to breathe and can cause the tissues in the throat to vibrate, leading to snoring.
9 Common Solutions That Can / Claim to Help You Stop Snoring

In the quest to address snoring, many solutions are touted as effective, each offering a unique approach to alleviating this common issue. From simple lifestyle modifications to advanced medical treatments, understanding the range of options available can help you find the most suitable method for your needs.
Exploring these solutions not only sheds light on their effectiveness but also highlights the importance of choosing the right approach based on your specific situation and underlying causes of snoring.
1. Lifestyle Changes
Weight Loss
Carrying excess weight, particularly around the neck, can lead to a narrower airway, increasing the likelihood of snoring. Shedding these extra pounds can alleviate this pressure, resulting in reduced snoring.
Avoiding Alcohol and Sedatives
Alcohol and sedatives relax the muscles in the throat, making it more likely for the airway to become obstructed during sleep. Steering clear of these substances before bedtime helps maintain muscle tone, reducing the risk of snoring.
Sleep Position
Sleeping on your back can cause the tongue and soft tissues to collapse into the throat, obstructing the airway. Sleeping on your side helps keep the airway open, preventing this collapse and reducing snoring.
Reality: Lifestyle modifications are among the most effective and sustainable ways to reduce snoring. While they require commitment and time to see results, combining these changes with other treatments often yields the best outcomes.
2. Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
These devices deliver a continuous stream of air through a mask worn during sleep, keeping the airway open and preventing the breathing pauses characteristic of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and severe snoring.
Reality: CPAP machines are considered the gold standard for treating OSA and severe snoring. They are highly effective but require a prescription and proper fitting by a healthcare professional. Some users may find them uncomfortable or inconvenient, which can impact adherence.
3. Anti-Snoring Devices
Mouthpieces and Nasal Strips
These over-the-counter devices work by adjusting the position of the jaw or physically opening the nasal passages to keep the airway unobstructed. Mandibular advancement devices (MADs) are a type of mouthpiece that moves the jaw forward to increase the space in the airway.
Nasal Decongestants
These medications can alleviate nasal congestion, making it easier to breathe through the nose and reducing the likelihood of mouth breathing, which often leads to snoring.
Reality: Anti-snoring devices can be effective for those with mild to moderate snoring. Nasal strips and decongestants are particularly useful for individuals whose snoring is exacerbated by nasal congestion.
Mouthpieces, especially MADs, can benefit those with anatomical obstructions in the throat. However, the effectiveness can vary, and some users may experience discomfort or difficulty adjusting to these devices.
4. Unregulated Supplements and Sprays
Many over-the-counter supplements and sprays are marketed as remedies for snoring, but they often lack rigorous scientific validation.
Reality: Without proper research and clinical trials, these products may not only fail to address snoring effectively but could also pose potential health risks. Since they are not regulated by health authorities, their ingredients and potential side effects can be unknown, making them a risky choice.
5. Snore Rings/Clips
These devices are designed to be worn in the nostrils or around the nose with the intention of widening nasal passages and improving airflow.
Reality: The effectiveness of these devices is often questionable. There is limited evidence to support their efficacy in reducing snoring, and they can be uncomfortable to wear, potentially leading to disruption of sleep rather than improvement.
6. Home Remedies
Throat Exercises
Engaging in throat exercises, also known as oropharyngeal exercises, can strengthen the muscles of the throat and tongue. This increased muscle tone can help prevent the airway from collapsing during sleep, potentially reducing snoring. Exercises may include vocalisations, swallowing exercises, or resistance training aimed at improving muscle control in the throat.
Essential Oils
Some individuals turn to essential oils, such as eucalyptus or peppermint, to alleviate nasal congestion and promote clearer breathing. The aromatic properties of these oils are believed to help open up nasal passages and ease airflow, which may help reduce snoring, especially if nasal congestion is a contributing factor.
Reality: Throat exercises can be beneficial, particularly when used in conjunction with other treatments. They require consistent practice to achieve noticeable results and may not be a standalone solution for everyone. The effectiveness of essential oils is largely anecdotal, with varying results among individuals.
7. "Miracle" Pillows
Various pillows are marketed with bold claims of curing snoring through their design.
Reality: While some pillows are engineered to encourage side sleeping—a position that can reduce snoring—they often come with exaggerated promises or unverified materials. It is important to be wary of any product that makes extraordinary claims without credible evidence. Instead, focus on pillows designed by reputable manufacturers that support proper sleep posture and comfort.
8. Surgical Interventions
Laser-Assisted Uvulopalatoplasty (LAUP)
LAUP is a surgical procedure that uses a laser to remove part of the soft palate and the uvula, the small, teardrop-shaped tissue hanging at the back of the throat. The goal is to enlarge the airway and reduce the vibrations that cause snoring. By removing or reshaping these tissues, LAUP aims to create a smoother airway passage, thereby alleviating snoring.
Other Surgeries
Several other surgical procedures can address structural issues contributing to snoring. For instance, correcting a deviated septum involves straightening the nasal septum, which can improve airflow and reduce snoring caused by nasal obstructions. Additionally, surgeries to remove excess throat tissue or tighten the muscles of the throat can help prevent the collapse of tissues that block the airway during sleep.
Reality: Surgical interventions are generally considered a last resort after other treatments have proven ineffective. While these procedures can be highly effective for some individuals, they also come with risks such as infection, bleeding, or anaesthesia complications.
Recovery time can vary, and there may be discomfort or changes in the throat’s anatomy that need adjustment. As such, these options are typically pursued with careful consideration and consultation with a healthcare professional.
9. Electrical Stimulation Devices
Some devices claim to reduce snoring through electrical stimulation of throat muscles.
Reality: However, these devices raise concerns about both safety and effectiveness. The electrical impulses may not be effective in addressing the root cause of snoring, and there is limited research on their long-term impacts. Using such devices without medical supervision can pose risks to your health.
免費體驗
Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
How Perfect Medical Can Help You to Solve Snoring

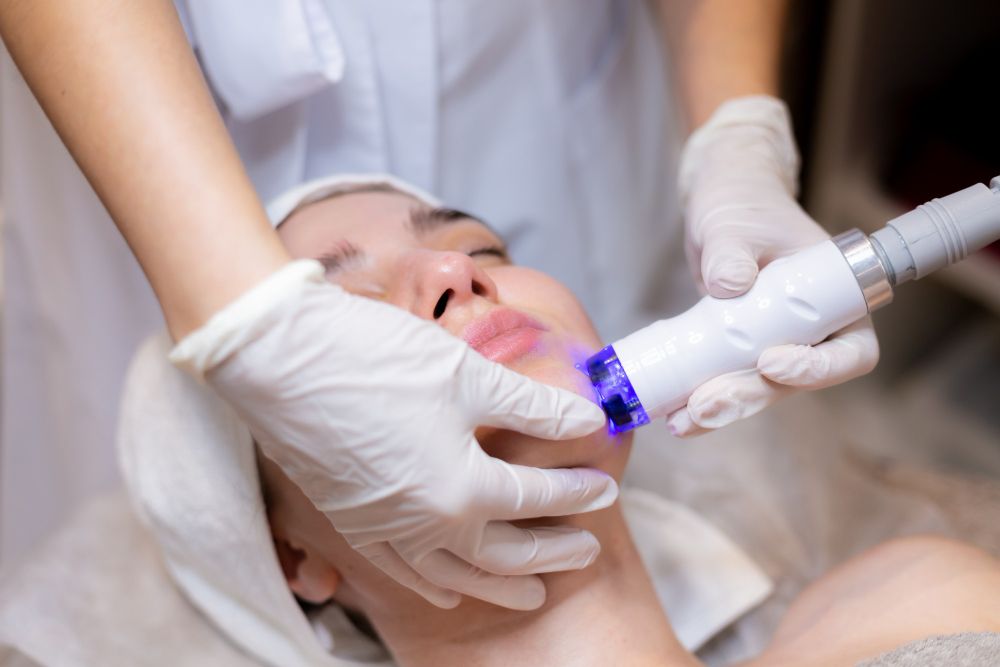
Perfect Medical's Fotona 4D NightLase treatment offers a promising non-invasive solution for snoring and sleep-related breathing issues. Unlike traditional methods that might require significant lifestyle changes or invasive procedures, Fotona's NightLase provides a cutting-edge approach that is both effective and gentle. Here’s an overview of how it works and its benefits:
Fotona 4D NightLase is a non-ablative laser therapy designed to address snoring by improving the tone and elasticity of the tissues in the throat. The treatment uses advanced laser technology to stimulate the tissues without removing or damaging them, making it a non-invasive option for individuals struggling with snoring or mild sleep apnea
1. Stimulation of Collagen Production
The NightLase treatment uses laser energy to gently heat the tissues of the throat, which stimulates the production of collagen. Collagen is a key protein that helps maintain the structural integrity and firmness of the tissues. By boosting collagen levels, NightLase helps to tighten and strengthen the soft palate and other areas of the throat, which can reduce the tendency of these tissues to collapse and obstruct the airway during sleep.
2. Enhanced Tissue Elasticity
The non-ablative laser technology employed in NightLase promotes increased elasticity in the treated tissues. This enhanced elasticity helps the throat muscles and soft palate maintain their shape and function better during sleep, thereby reducing snoring.
Unlike ablative treatments that remove or resurface tissues, non-ablative lasers work beneath the surface, leaving the outer layer intact and minimising recovery time.
3. Comfort and Convenience
Since NightLase is non-ablative, the procedure is typically more comfortable and involves less downtime compared to invasive treatments. Patients often report minimal discomfort and can resume normal activities shortly after the procedure. The non-ablative nature of the treatment also reduces the risk of complications and adverse effects.
4. Multiple Sessions for Optimal Results
To achieve the best outcomes, a series of NightLase sessions may be recommended. Each session helps to progressively improve tissue tone and airway function, leading to more significant and long-lasting results over time. The treatment plan is personalised based on the individual’s specific needs and response to the therapy.
Benefits of Fotona 4D NightLase
• Non-Invasive: No need for surgical procedures or extensive recovery time.
• Effective: Helps improve tissue tone and elasticity, reducing snoring.
• Minimal Discomfort: The procedure is generally well-tolerated with few side effects.
• Convenient: Requires no downtime, allowing patients to return to their daily routines immediately.
Talk to Us to Learn How to Stop Snoring Today!
Fotona 4D NightLase treatment is an innovative and effective solution for managing snoring, particularly when traditional methods have proven inadequate. Its non-ablative laser technology offers a comfortable and efficient alternative, targeting the root causes of snoring by enhancing the tone and elasticity of the throat tissues. If you are looking for a non-invasive approach to reduce snoring and improve sleep quality, talk to us!
Perfect Medical's Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment免費體驗
Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

1. What is one thing you can do to reduce snoring while you sleep?
One effective approach is to sleep on your side. When you sleep on your back, your tongue and soft tissues can fall to the back of your throat, causing snoring. Sleeping on your side can help keep your airway open and reduce snoring.
2. How can sleeping on your side help with snoring?
Sleeping on your side can significantly help reduce snoring by addressing the common issue of airway obstruction. When you sleep on your back, gravity can cause the tongue and soft tissues in your throat to fall backward, partially blocking the airway. This obstruction creates turbulence in the airflow, which leads to the vibration of the throat tissues and results in snoring.
3. If you snore, what can you do to improve your sleep quality?
To improve your sleep quality and reduce snoring, you can consider strategies such as maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding alcohol before bedtime, and using nasal decongestants if nasal congestion contributes to your snoring. These combined efforts can significantly improve your sleep quality and reduce the disruptive effects of snoring.
4. How can a patient's sleeping position influence snoring?
A patient's sleeping position significantly influences snoring. If you sleep on your back, your tongue and soft tissues can fall into the back of your throat, which may obstruct the airway and cause snoring. Sleeping on your side helps keep these tissues away from the airway and can reduce snoring.
5. What are some things you can do to address snoring if you sleep on your back?
If you sleep on your back and snore, consider changing your sleeping position to your side. This adjustment can help prevent your tongue and throat tissues from falling to the back of your throat, which can reduce snoring and improve your sleep quality.