- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets

免費體驗
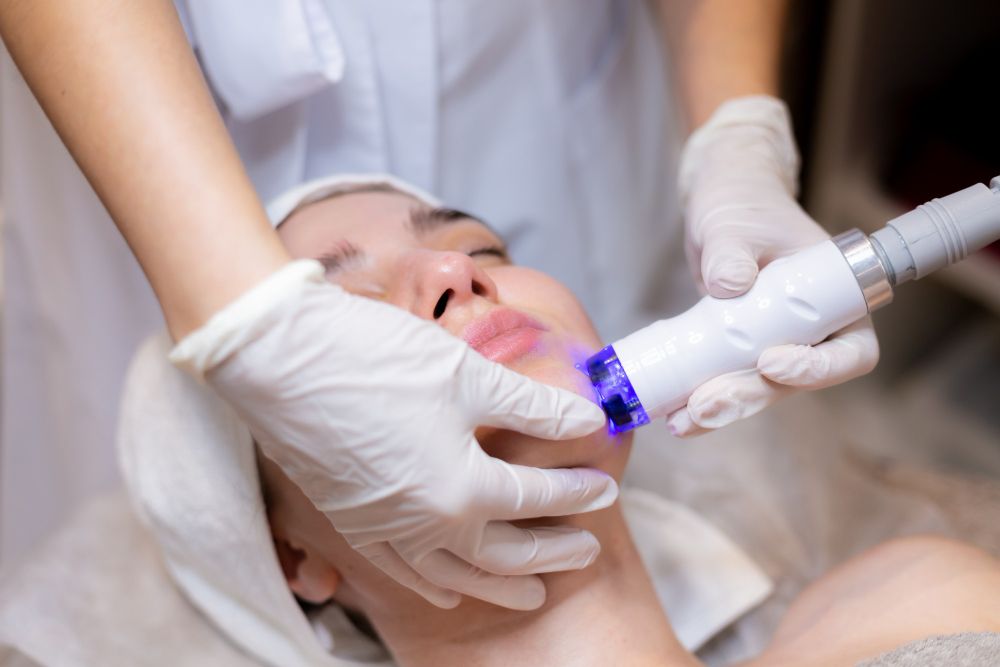
Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Sleep apnea is a prevalent sleep disorder characterised by breathing interruptions during sleep. These pauses can range from mild to severe, causing a dip in blood oxygen levels and disrupting your sleep quality. Let's take a deeper look at the condition and how you can improve your sleep.
1
Types of Sleep Apnea

Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA)
2
5 Sleep Apnea Symptoms

1. Loud Snoring
2. Daytime Sleepiness
3. Frequent Awakenings
4. Morning Headaches
5. Difficulty Concentrating
3
What Are the Risks When Obstructive Sleep Apnea Occurs?

1. High Blood Pressure
2. Heart Disease
3. Stroke
4. Type 2 Diabetes
4
Can Sleep Apnea Be Cured? Taking Control of Your Sleep

Utilising the Science Behind Fotona 4D NightLase: A Gentle Approach to Snoring Relief

免費體驗
Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
5
Conclusion


免費體驗
Fotona 4D NightLase Snoring Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

1. How can losing weight impact sleep apnea?
Losing weight can have a profound impact on sleep apnea by reducing symptoms, particularly in cases where excess weight contributes to airway blockage or the enlargement of soft tissues in the upper airway. Excessive weight can put pressure on the neck and throat area, leading to obstruction during sleep. By shedding excess pounds, the airway can become less obstructed, resulting in improved breathing and reduced instances of interrupted sleep typical of sleep apnea.
2. When should I see a sleep specialist for sleep apnea?
If you're experiencing symptoms such as loud snoring, daytime sleepiness, or suspect you have sleep apnea due to risk factors like obesity or a family history of the condition, it's crucial to seek the expertise of a sleep specialist. Sleep specialists are trained to diagnose and manage sleep disorders like sleep apnea through comprehensive evaluations, which may include sleep studies to assess breathing patterns and oxygen levels during sleep. Early intervention with a specialist can lead to more effective management and improved quality of life.
3. What is CPAP therapy and how does it treat sleep apnea?
CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) therapy is a standard treatment for sleep apnea that involves wearing a mask connected to a machine delivering pressurised air. This pressurised air keeps the airway open during sleep, preventing obstruction and allowing for uninterrupted breathing. CPAP therapy is highly effective in treating sleep apnea, and its success is often attributed to its ability to maintain consistent airflow, thereby reducing apnea episodes, improving oxygenation, and promoting restful sleep.
4. Can oral appliances help in managing sleep apnea?
Oral appliances, such as mandibular advancement devices, play a valuable role in managing mild to moderate obstructive sleep apnea. These devices work by repositioning the lower jaw slightly forward during sleep, which helps keep the airway open and prevents collapse or obstruction. They are especially beneficial for individuals who cannot tolerate CPAP therapy or prefer a less invasive treatment option.
5. How does obstructive sleep apnea worsen over time?
Untreated obstructive sleep apnea can worsen over time due to repeated episodes of interrupted breathing, leading to increased risks of cardiovascular problems, hypertension, and other health complications.