- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets
免費體驗
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
The World Health Organization (WHO) aims to eliminate industrially produced trans fats from the global food supply by 2023, striving to reduce the worldwide burden of cardiovascular diseases. Trans fats are a type of unsaturated fat that pose significant health hazards. This article delves into the nature of trans fats, their adverse health effects, what you should do to keep your intake of trans fat in control, and how you can get rid of your body fats
What are Trans Fats?

Trans fats, which come in different forms, play a significant role in both processed foods and naturally occurring sources. Let’s explore the definitions and types of trans fats to better grasp their impact on health.
Trans Fatty Acids
Trans fats, also known as trans fatty acids, are a type of unsaturated fat that undergoes a chemical process called hydrogenation. This process adds hydrogen atoms to liquid vegetable oils, converting them into a solid or semi-solid state.
The result is a type of fat that is more stable and less likely to spoil, but it has been linked to several health issues.
Partially Hydrogenated Oils
The majority of trans fats found in food are created through an industrial process called partial hydrogenation. This method involves adding hydrogen to vegetable oils to make them more solid and increase their shelf life. The partially hydrogenated oils are commonly used in processed foods to enhance texture, improve flavour stability, and prolong shelf life.
Examples include certain margarine, baked goods, and snack foods. This type of trans fat is particularly harmful and has been associated with increased risks of heart disease.
Naturally Occurring Trans Fats
Trans fats are also present in small amounts in some animal products. These naturally occurring trans fats are produced by the digestive processes of ruminant animals, such as cows and sheep. They are found in meat and dairy products, such as beef, lamb, and dairy products like milk and cheese.
Although these naturally occurring trans fats are present in much smaller quantities than industrial trans fats, they are still subject to ongoing research regarding their health effects.
Trans Fats in Weight Gain: How Does It Make You Turn Fat?

Trans fats can have a profound effect on your body composition and appearance, primarily by promoting an increase in body fat. Here's an in-depth look at how these fats influence your physique:
1. Altered Fat Distribution
One of the notable effects of trans fats is their impact on fat distribution. Regular consumption of trans fats has been shown to encourage fat accumulation in the abdominal area.
This type of fat, often referred to as visceral fat, not only contributes to a bulging belly but is also associated with higher health risks, including cardiovascular disease and metabolic disorders. The redistribution of fat to the abdomen makes it more visible and accentuates the appearance of excess body fat.
2. Increased Fat Storage
Trans fats contribute to excessive fat accumulation by altering how your body stores fat. Unlike other dietary fats, trans fats are particularly effective at promoting fat storage.
They also influence the body's mechanisms to increase fat deposits, especially in the abdominal and thigh regions. This leads to a noticeable rise in overall body fat, making areas like the belly and hips appear more pronounced.
3. Impaired Metabolism
Trans fats disrupt your body's metabolic processes, leading to detrimental effects on your overall health. They are known to cause insulin resistance, which impairs the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels effectively.
This metabolic disturbance can result in weight gain as the body becomes less efficient at burning calories. Over time, this can lead to an increase in body fat, especially if combined with a calorie-dense diet.
4. Increased Appetite
Another significant effect of trans fats is their impact on appetite regulation. They interfere with the hormones responsible for hunger and satiety, causing an increase in appetite.
As a result, you may find yourself eating more than necessary, leading to an excess calorie intake. Consuming more calories than you burn inevitably leads to weight gain and increased body fat accumulation.
5. Inflammation and Cell Function
Trans fats are known to promote inflammation within the body, which can have a cascading effect on your ability to manage body fat. Inflammation can disrupt normal cellular function and impair the body's fat-burning processes.
This inflammatory response can make it more difficult for your body to efficiently metabolise fat, resulting in a higher accumulation of fat in various body parts, contributing to an overall increase in body fat and a less toned appearance.
Health Risks Linked to Excessive Intake of Trans Fats

Consuming excessive amounts of trans fats can have significant detrimental effects on your health, beyond just affecting your body composition. Here's a closer look at the various health risks associated with high trans fat intake:
Chronic Inflammation
Trans fats have been shown to significantly contribute to chronic inflammation, a condition where the body's immune system remains persistently activated. This ongoing inflammatory state is a key factor in the development and progression of various chronic diseases. Here’s how trans fats impact inflammation and the related health risks:
Heart Disease:-
Plaque Formation: Inflammation in the arteries promotes the buildup of plaque, a combination of fatty deposits, cholesterol, and other substances. This plaque can narrow and harden the arteries, leading to atherosclerosis. As the arterial walls become inflamed and damaged, the risk of heart disease increases, potentially leading to serious conditions such as heart attacks and strokes.
Diabetes:-
Impaired Insulin Function: Chronic inflammation caused by trans fats negatively affects insulin sensitivity. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into cells. When inflammation impairs insulin function, it leads to insulin resistance, a condition where the body's cells do not respond properly to insulin. This resistance results in elevated blood sugar levels, which can progress to type 2 diabetes over time.
Cancer:-
Cancer Development: Persistent inflammation is a known risk factor for certain types of cancer. Chronic inflammation can create an environment that promotes cellular damage and mutations. This ongoing inflammatory response can disrupt normal cell growth and repair processes, potentially leading to cancerous changes in cells.
Overall Impact on Health:-
Immune System Disruption: Trans fats not only cause localised inflammation but also disrupt the overall functioning of the immune system. A chronically activated immune system can lead to an overproduction of inflammatory molecules, such as cytokines, which contribute to systemic inflammation. This systemic inflammation affects multiple organs and systems, increasing the risk of various chronic diseases beyond heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Obesity
Trans fats play a significant role in weight gain and the development of obesity through several mechanisms:
Promotion of Fat Accumulation:-
Trans fats are notorious for their role in encouraging fat accumulation in the body. Unlike other types of fats, trans fats are readily stored in fat cells rather than being used for energy. This propensity to accumulate fat contributes to an increase in overall body fat and is particularly linked to the storage of fat in the abdominal area, leading to a more pronounced "belly" appearance.
Disruption of Metabolic Processes:-
Trans fats negatively impact metabolic processes, leading to various metabolic disturbances. They interfere with the body's ability to efficiently process and utilise fats, leading to increased fat storage. Additionally, trans fats can contribute to insulin resistance, a condition where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin, resulting in higher blood sugar levels and promoting further fat accumulation.
Increased Appetite and Overeating:-
Consumption of trans fats can affect hunger and satiety signals in the brain. They often lead to an increased appetite, causing individuals to consume more calories than necessary. This overeating exacerbates weight gain and contributes to the development of obesity. The high calorie density of foods containing trans fats further compounds this issue, as they contribute to excess calorie intake without providing substantial nutritional benefits.
Inflammatory Effects:-
Trans fats are known to promote inflammation in the body. Chronic inflammation is associated with the development of obesity and can lead to an increased accumulation of fat. Inflammation affects the body’s ability to regulate fat storage and utilisation, leading to further weight gain and difficulties in managing body weight.
Beyond contributing to weight gain, trans fats also negatively impact overall health. They are linked to various health issues such as cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome, all of which can exacerbate the challenges of managing and reducing obesity. The cumulative effect of these health issues further complicates weight management and contributes to the persistence of obesity.
3 Strategies to Minimise Your Trans Fat Intake

Trans fats pose significant health risks, including increased inflammation and the development of chronic diseases. Adopting strategies to minimise trans fat intake is crucial for maintaining optimal health. Here are some practical approaches to help you reduce trans fats in your diet:
1. Reading Labels
- Scrutinise Nutrition Labels: One of the most effective ways to limit trans fat consumption is by carefully examining food labels. Manufacturers are required to list trans fats on the nutrition facts panel, often under "Total Fat" or specifically as "Trans Fat." Look for products that contain "partially hydrogenated oils" in the ingredients list, as these are a primary source of artificial trans fats. Opt for items that list zero trans fats and avoid those with partially hydrogenated oils.
- Be Wary of Marketing Claims: Some products may claim to be "trans fat-free" but still contain small amounts of trans fats. Ensure that the nutrition label confirms this claim by listing "0 grams" of trans fat per serving.
2. Healthier Choices
- Opt for Unsaturated Fats: Replace trans fats with healthier fats, such as unsaturated fats, which are beneficial for heart health. Incorporate foods rich in unsaturated fats into your diet, including:
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are excellent sources of unsaturated fats.
- Avocados: Rich in monounsaturated fats, avocados can help improve cholesterol levels and provide essential nutrients.
- Olive Oil: Use extra virgin olive oil as a cooking oil or salad dressing to benefit from its heart-healthy monounsaturated fats.
- Select Lean Proteins: Opt for lean meats, poultry, and fish over processed meats that may contain trans fats. Including sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and sardines, can also support heart health.
3. Balanced Diet and Exercise
- Adopt a Nutritious Diet: Focus on a well-rounded diet that emphasises.
- Fruits and Vegetables: High in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, these foods help combat inflammation and support overall health.
- Whole Grains: Choose whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat over refined grains. Whole grains provide essential nutrients and fibre that aid in digestion and regulate blood sugar levels.
- Lean Proteins: Incorporate sources of lean protein, such as beans, lentils, tofu, and poultry, to build muscle and maintain a healthy metabolism.
- Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Combine a balanced diet with consistent exercise to enhance overall health and manage body weight. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity each week, alongside muscle-strengthening exercises.
免費體驗
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
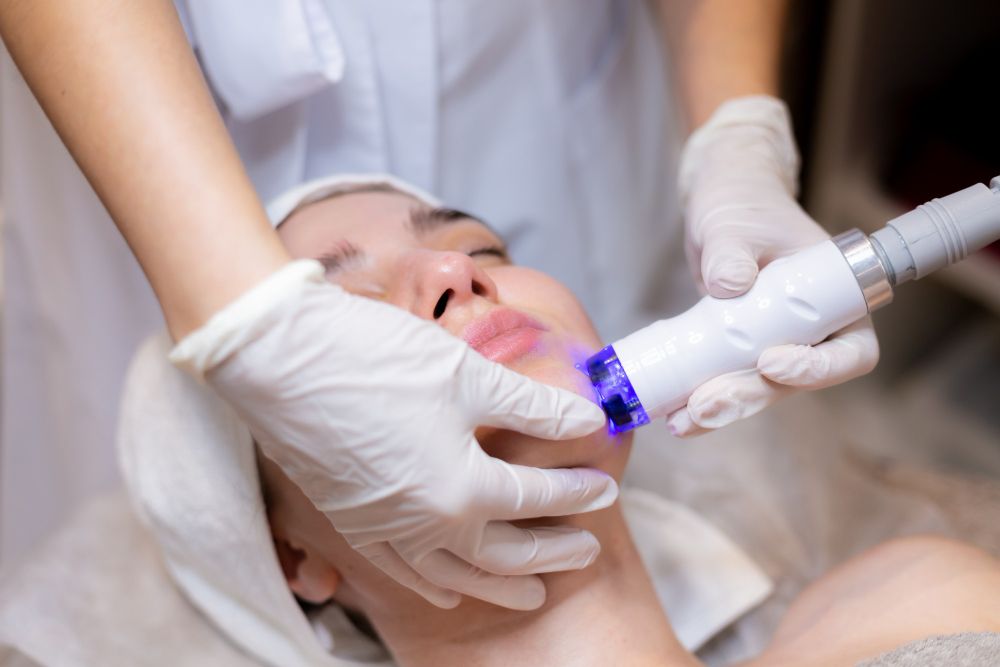
Enhancing Health with S6 Body Sculpting Treatment

While making dietary adjustments is vital for reducing trans fats and improving overall health, integrating advanced treatments like the S6 Body Sculpting Treatment can provide significant support in your journey toward a healthier body!
Perfect Medical’s S6 Body Sculpting Treatment represents a sophisticated approach to tackling stubborn fat that dietary changes alone may not fully address. This treatment employs state-of-the-art bio-laser and vacuum suction technology, specifically designed to target and diminish fat deposits, including those problematic visceral fats that can adversely affect cardiovascular health.
Mechanism of Action
The S6 Body Sculpting Treatment operates through a dual-action process. Bio-lasers are utilised to break down fat cells, effectively releasing fatty acids from these cells. Subsequently, vacuum suction technology facilitates the natural drainage of these fatty acids through the lymphatic system.
This method not only reduces fat in targeted areas but also promotes overall health benefits by addressing fat deposits that are often linked to higher cholesterol levels and poor blood circulation.
Target Areas
This treatment is especially effective in targeting key areas where fat accumulation is most prevalent, such as the abdomen, waist, and thighs. Excess fat in these regions is particularly concerning due to its impact on heart health, making the S6 Body Sculpting Treatment a valuable tool in mitigating these risks.
Get Rid of Trans Fats in Your Body and Regain Slim Body Now!

While dietary modifications play a fundamental role, stay informed about the dangers of trans fats and make conscious dietary choices to protect your heart health. For those seeking additional support, the S6 Body Sculpting Treatment offers a promising solution for reducing harmful fat deposits and fostering a healthier body. Embrace this comprehensive approach to health management and commit to a brighter, more vibrant future today! Book your appointment now:
Perfect Medical‘s S6 Body Sculpting Treatment免費體驗
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

1. What is the Food and Drug Administration's stance on trans fats in food?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requires that the amount of trans fats be listed on nutrition labels. If a food product contains less than 0.5 grams of trans fat per serving, it can be labelled as containing 0 grams of trans fat. The FDA has also implemented regulations to limit the use of hydrogenated vegetable oils in food products due to their high trans fat content.
2. How do saturated fats and trans fats affect my health?
Saturated and trans fats are both linked to increased health risks, including heart disease. Saturated fats can raise levels of LDL (bad) cholesterol in the blood, while trans fats not only increase LDL cholesterol but also decrease HDL (good) cholesterol. Trans fats are particularly harmful as they can promote inflammation and lead to a higher risk of coronary artery disease.
3. How can I tell if a food product contains trans fats?
To determine if a food product contains trans fats, check the nutrition label for the amount of trans fat listed per serving. Be aware that hydrogenated vegetable oils are a key source of trans fats. If the label lists partially hydrogenated oils among the ingredients, it indicates the presence of trans fats. Even if the label states 0 grams of trans fat, the product may still contain less than 0.5 grams per serving, which can add up if consumed in large quantities.
4. What is the recommended limit for trans fat intake according to health guidelines?
Health guidelines suggest that the amount of trans fats consumed should be as low as possible, about less than 1% of total fat intake. This translates to avoiding foods with high levels of hydrogenated vegetable oils and choosing products with healthier fats, such as essential fatty acids found in nuts, seeds, and fish.
5. How do hydrogenated vegetable oils contribute to the amount of trans fats in my diet?
Hydrogenated vegetable oils are a major source of trans fats in many processed foods. The process of hydrogenation converts liquid vegetable oils into a solid form, increasing the amount of trans fats in the oil. These trans fats are harmful as they contribute to elevated LDL cholesterol levels and decrease HDL cholesterol, increasing the risk of heart disease.