- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets

免費體驗
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Avocados, with their creamy texture and unique flavour, have become a beloved fruit in many households. Despite their popularity, questions often arise about their impact on weight management due to their reputation as a high-fat food. In this article, we will delve into the nutritional profile of avocados, their potential effects on weight, and their overall contribution to health. From monounsaturated fats to heart-healthy benefits, let's uncover the truth about avocados and explore their role in promoting optimal well-being.
1
Avocado Nutrition Unveiled: How Many Calories In 1 Avocado?
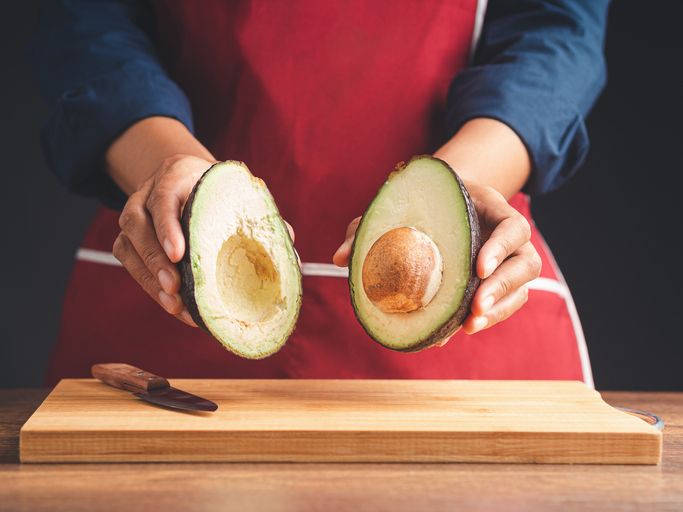

1. Monounsaturated Fats
2. Dietary Fibre
3. Vitamins
4. Minerals
5. Antioxidants
6. Protein
7. Phytosterols

2
Bad Fats Good Fats: Monounsaturated Fats and Healthy Fats
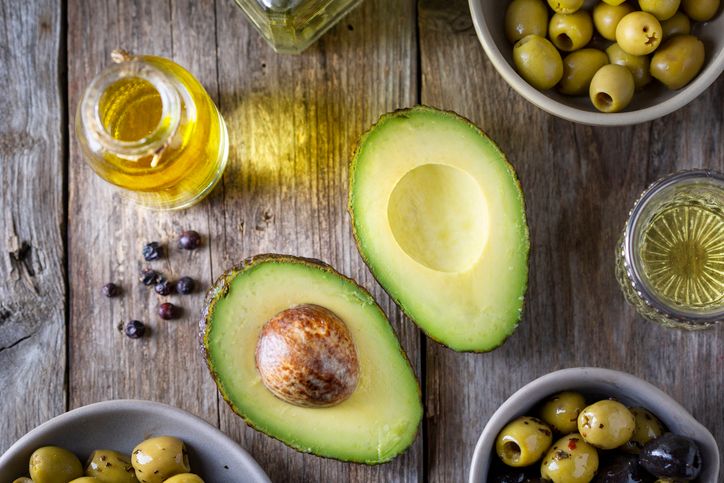

Bad Fats
Monounsaturated Fats and Healthy Fats
Key Differences:
3
Weight Gain vs. Weight Loss: How Can Avocado Help to Lose Weight?
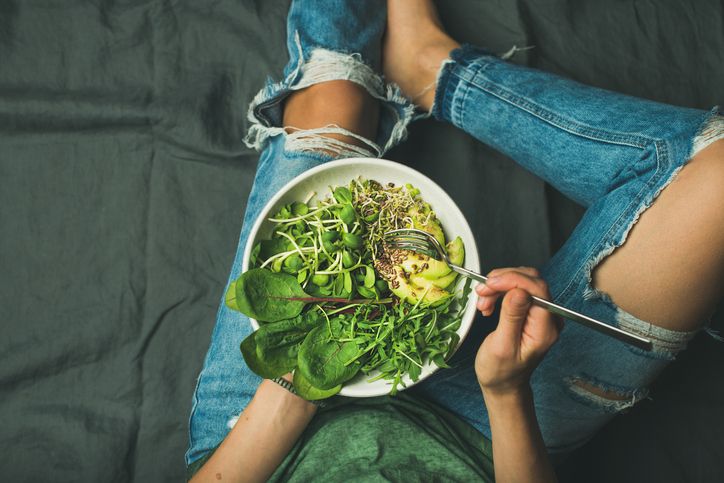

Caloric Content and Portion Control
Healthy Fats and Satiety
Metabolic Benefits and Heart Health
Impact on Obesity-Related Conditions

4
3 Delicious Avocado Recipe for Your Healthy Fat Diet

Avocado Toast with Egg
Avocado and Chickpea Salad
Avocado Smoothie
免費體驗
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
5
Eat Avocado With Cautious: What Happens If I Eat Too Much Of Them?

Caloric Intake
Fat Content
Fibre Intake
Oxalate Content
Allergies
Interference with Medications

6
Not A Fan of Avocado? Try These So You Won't Have to Gain Weight

Olive oil
Nuts and Seeds
Fatty Fish
Nut Butters
Seeds and Avocado Oil
Dark Chocolate
Tofu and Edamame
Flaxseed Oil
- You Should Do These 10 Best Back Workouts for a Slim, Toned, Strong Back
- 16 Best Belly Fat Exercises to Help You Lose Belly Fat and Strengthen Abdominal Muscles, Science-Proven!
- Understanding Cortisol and Its Impact on Weight: Effective Strategies to Manage Cortisol Levels for Weight Loss
- Jump Rope Weight Loss: 8 Benefits Of Jump Rope + Complete Beginner's Guide
7
Like to Eat Foods That are High in Fat? Let Perfect Medical Take Care of It For You!


8
Conclusion

免費體驗
S6 Body Sculpting Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

1. How can I prevent weight gain while still enjoying mashed avocado in my meals?
Balancing your overall calorie intake, including only one avocado in your servings, and incorporating other nutrient-dense foods can help prevent weight gain while enjoying the goodness of mashed avocado.
2. Can overweight and obese people benefit from eating avocado as part of their diet?
Yes, incorporating moderate amounts of avocado into a well-balanced diet can be beneficial for overweight and obese individuals. The monounsaturated fats in avocados may contribute to heart health, and their fibre content can aid in satiety.
3. How does eating avocado help in weight management for those looking to prevent weight gain?
Eating avocado in moderation can support weight management by providing healthy fats and fibre, promoting a feeling of fullness and satisfaction, which may help prevent overeating and weight gain.
4. Is it advisable to consume more than one avocado daily for its health benefits?
While avocados offer numerous health benefits, including one avocado in your daily diet is generally recommended. Consuming excessive amounts may lead to a higher calorie intake, potentially contributing to weight gain.
5. Can incorporating one avocado a day contribute to weight loss for overweight individuals?
Including one avocado a day as part of a calorie-controlled diet may support weight loss efforts for overweight individuals. The nutrient density and satiating properties of avocados can enhance overall dietary satisfaction while managing calorie intake.