- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets

免費體驗
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
The warm embrace of sunlight can be delightful, but its effects on our skin can be profound, sometimes leading to serious concerns like sun damage and skin cancer. Let's talk about the intricacies of sun exposure and its impact on our skin health!
1
Science Breakdown: What is Ultraviolet Radiation (UV)?
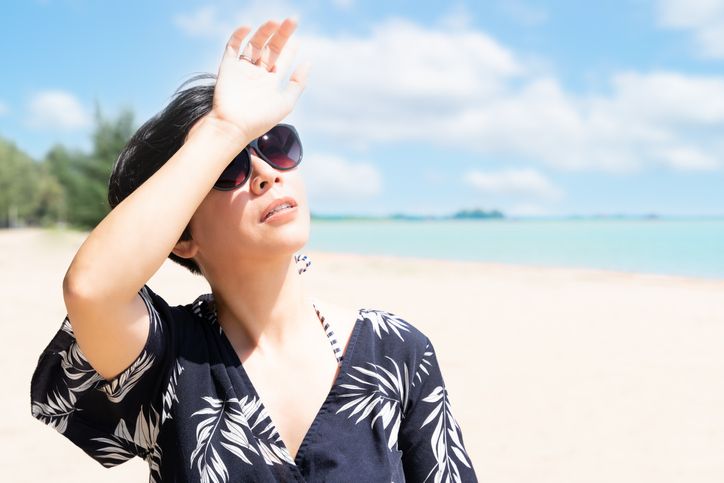

1. Ultraviolet A (UVA) Rays
2. Ultraviolet B (UVB) Rays
3. Ultraviolet C (UVC) Rays
2
5 Critical Impacts of Sun Damage on Skin Health
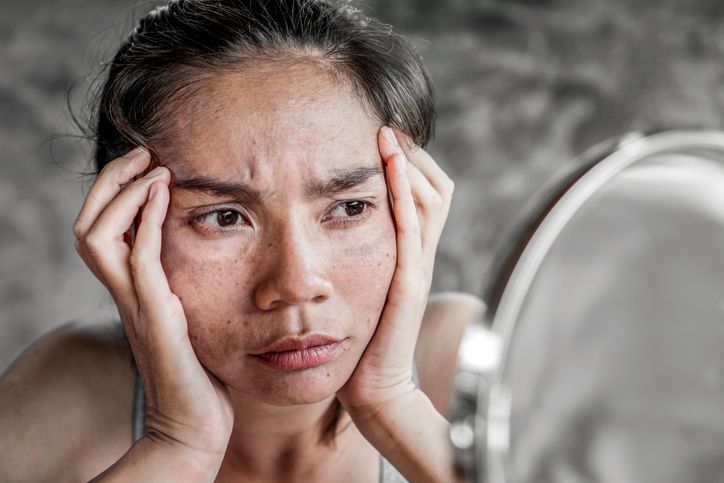

1. Premature Ageing
2. Skin Cancer Risk
3. Photodamage and Structural Changes
4. Actinic Keratosis and Precancerous Lesions
5. Impact on Immune Function
- PicoSure Pro Laser Guide – 4 Key Benefits You Should Know! Is It Different from Regular Pico Laser?
- Honeycomb Pico Laser Editor-Trial: Effect on Hormonal Spots, and How it Differs from Regular Pico Laser
- How to Choose Dark Spot Correctors: 5 Powerful Pigment-Fading Ingredients + 14 Recommended Serums for Visible Results
- Benign And Malignant Pigmented Lesions: The Risks and Realities
3
15 Useful Tips to Protect Sun Exposed Areas Extensively
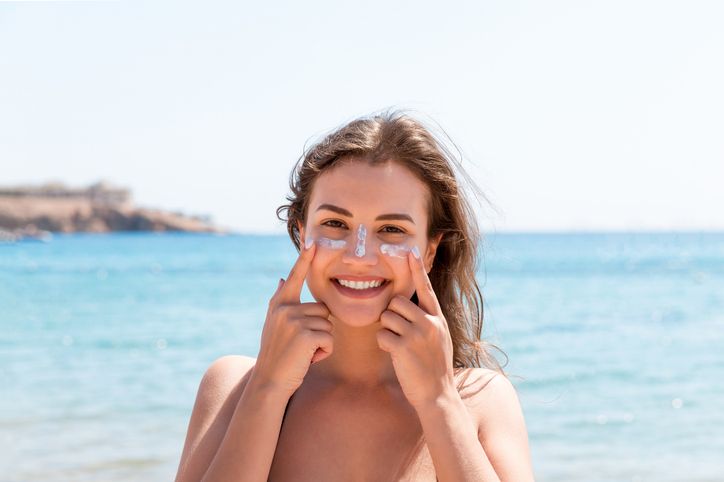

1. Sunscreen is Your Best Friend
2. Sun Protection Clothing is Essential
3. Accessorise for Sun Safety
4. Hydration for Skin Resilience
5. Don't Forget Your Lips
6. Be Sun Smart After Sun Exposure
7. Exfoliate Regularly
8. Diet Plays a Role
9. Beware of Medications
10. Know Your Skin Type
11. Self-Examination is Key
12. Avoid Tanning Beds
13. Sunglasses Indoors (Sometimes)
14. Sun Safety is a Year-Round Commitment
15. Seek Shade for Added Protection

4
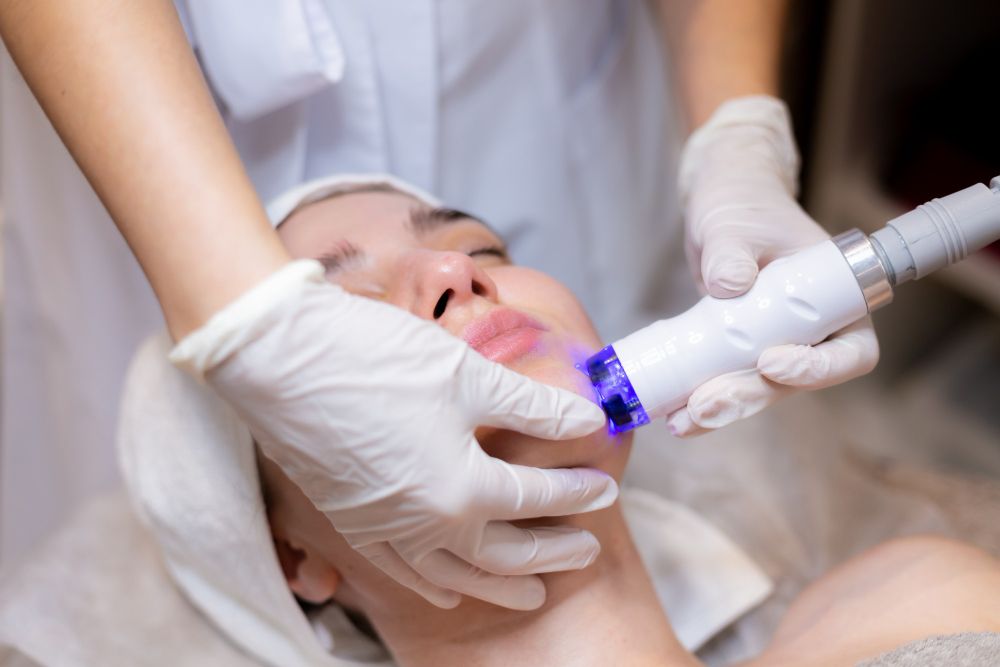
Tackling Aftermath of Sun Damage: PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment

Tailored for Asian Skin Tones
Eliminates Skin Discoloration without Rebound
FDA-Cleared and Minimally Invasive
Noticeable Reduction in Dark Spots

免費體驗
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

1. What role does sun protection factor (SPF) play in preventing skin damage from UV rays?
Sun protection factor (SPF) is crucial for shielding the skin from harmful UV rays, particularly UVB rays that cause sunburn and contribute to skin cancer risk. Higher SPF values indicate greater protection against UVB rays, but comprehensive sun protection requires broad-spectrum sunscreens that also defend against UVA rays. Broad-spectrum sunscreens, coupled with sun safety practices like seeking shade and wearing protective clothing, help minimise the risks associated with excessive sun exposure, including premature ageing and skin cancer.
2. How can you effectively reverse sun damage and improve your skin's health?
Sun damage reversal involves a multifaceted approach, including skincare products with ingredients like retinoids, antioxidants, and hyaluronic acid to boost collagen production, repair skin texture, and reduce hyperpigmentation. Additionally, procedures like laser therapy, chemical peels, and microneedling target specific sun-related concerns such as sunspots, wrinkles, and uneven skin tone, promoting skin rejuvenation and health.
3. What are the risks associated with excessive sun exposure and how can they be minimised?
Excessive sun exposure poses various risks, from sunburn and premature ageing to skin cancer and eye damage. Minimising these risks involves practising sun safety measures such as wearing sunscreen with a high SPF, seeking shade during peak sun hours, wearing protective clothing, sunglasses, and avoiding tanning beds. Regular skin cancer screenings and sun protection habits play crucial roles in reducing the adverse effects of sun exposure.
4. What are the key factors to consider when choosing a sunscreen to protect against sun damage?
When selecting a sunscreen for sun protection, several factors are crucial. Look for sunscreens labelled as broad-spectrum, indicating protection against both UVA and UVB rays. Choose a sunscreen with a high sun protection factor (SPF) of 30 or higher for adequate protection. Water-resistant formulas are ideal for outdoor activities or swimming. Additionally, consider your skin type and any sensitivities to ingredients like fragrances or preservatives when choosing a sunscreen for optimal sun protection and skin health.
5. What are the most effective treatments available to treat wrinkles caused by sun damage and ageing?
Effective treatments for sun-damaged wrinkles include topical retinoids, dermal fillers, botox injections, chemical peels, and laser resurfacing. These treatments target collagen stimulation, improve skin elasticity, and diminish fine lines and wrinkles. Consulting with a skincare professional helps determine personalised treatment plans tailored to individual skin concerns and goals for optimal results in sun damage reversal and wrinkle reduction.