- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets

免費體驗
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Struggling with stubborn dark patches on your skin? You're not alone. Melasma, characterised by dark patches on the skin, is a common condition that affects individuals of various skin tones. This article will equip you with the knowledge and actionable tips to effectively manage melasma with the help of melasma cream. Understanding the intricacies of melasma and its treatment is crucial for anyone dealing with this challenging skin concern. In this article, we delve deep into the world of melasma cream, skin tone management, and effective treatments to combat this condition.
1
What is Melasma?

1. Skin Tone
2. Hormonal Factors
3. Sun Exposure
4. Genetics
5. Gender
6. Cosmetic Procedures
7. Stress
2
4 Key Active Ingredients for Melasma Cream

1. Vitamin C
2. Tranexamic Acid
3. Lactic Acid
4. Ferulic Acid
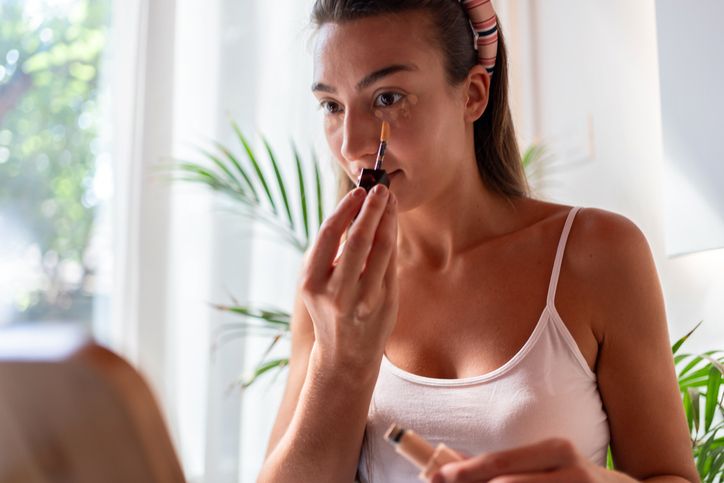
Steps To Use it Correctly
3
3 Other Effective Options to Treat Melasma

1. Topical Treatments
2. Sun Protection
3. Medical Interventions
4
Closing Thoughts


免費體驗
PicoCure Pigmentation Removal Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

1. What are some topical agents commonly used in melasma treatment?
Topical agents such as hydroquinone, kojic acid, and azelaic acid are commonly used in melasma treatment. These ingredients work by inhibiting melanin production, which is responsible for dark spots and hyperpigmentation. Hydroquinone is a well-known skin lightening agent that blocks the enzyme involved in melanin production. Kojic acid, derived from fungi, also inhibits melanin synthesis by chelating copper ions necessary for melanin formation. Azelaic acid has both antimelanogenic and anti-inflammatory properties, making it effective for treating melasma and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
2. How does hormonal birth control affect melasma and the skin barrier?
Hormonal birth control, especially oestrogen-based contraceptives, can influence melasma due to their impact on hormone levels. Oestrogen can stimulate melanocyte activity, leading to increased pigmentation. Progesterone, another hormone in some contraceptives, can also contribute to melasma by promoting blood vessel dilation and increasing melanin production. These hormonal changes can disrupt the skin barrier, making it more susceptible to pigmentation issues and UV damage.
3. What role does collagen production stimulation play in achieving an even skin tone?
Collagen is a key protein responsible for skin elasticity and firmness. Stimulating collagen production can help improve skin texture and contribute to a more even skin tone. Ingredients like vitamin C and retinoids are known collagen boosters. Vitamin C promotes collagen synthesis and also has antioxidant properties that protect the skin from oxidative stress, which can lead to uneven skin tone and pigmentation. Retinoids, derivatives of vitamin A, increase cell turnover and collagen production, resulting in smoother and more even-toned skin over time.
4. How can protective clothing help prevent epidermal melasma?
Epidermal melasma is often triggered or worsened by UV radiation. Protective clothing, such as wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses, and clothing with UPF (Ultraviolet Protection Factor) ratings, can provide physical protection from UV rays. This reduces the risk of melanin production and hyperpigmentation triggered by sun exposure. Wearing protective clothing, along with applying broad-spectrum sunscreen, is crucial for preventing melasma and maintaining skin health.
5. What are some effective strategies for maintaining a healthy skin barrier while using skin lightening agents?
Skin lightening agents like hydroquinone or retinoids can sometimes compromise the skin barrier, leading to dryness, irritation, and increased sensitivity. To maintain a healthy skin barrier while using these agents, it's important to use gentle cleansers that do not strip the skin of its natural oils. Moisturisers containing ingredients like ceramides, hyaluronic acid, and fatty acids help restore and strengthen the skin barrier. Additionally, incorporating antioxidant-rich serums and avoiding harsh exfoliants can support skin health while targeting pigmentation issues.