- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets

免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
Acne is a widespread skin issue that affects many people, causing both physical discomfort and emotional stress. In the range of treatments available, doxycycline, an oral antibiotic, has become a popular choice, particularly for those dealing with moderate to severe acne. In this discussion, we'll take a closer look at doxycycline, including how it works, how to use it properly, and important points to consider while undergoing treatment. Let's dive into the details to better understand this acne-fighting option.
1
Doxycycline's Role in Acne Treatment

2
How Can Doxycycline Treat Acne?
Anti-inflammatory Properties
3
How Does Doxycycline Treats Acne?
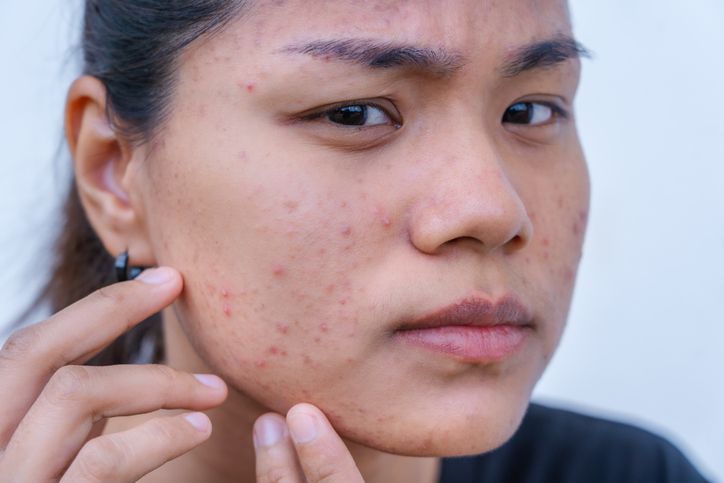
Doxycycline vs. Other Acne Medications

4
Who Can't Use Doxycycline for Acne? Potential Side Effects and Considerations

Common Side Effects
Common Side Effects of Doxycycline
More Serious Concerns Linked to Doxycycline
Who Should Be Cautious About Using Doxycycline?

免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
5
Not a Permanent Solution: Antibiotic Resistance Risk Behind Doxycycline
The Implications for Acne Treatment

6
4 Other Ways To Treat Acne Aside from Doxycycline

1. Hormonal Therapies for Acne
2. Chemical Peels for Acne
3. Light and Laser Therapy for Acne
4. The Acne Treatment by Perfect Medical
- How To Choose The Right Acne Patch? Learn Proper Usage + Effective Acne Solution
- Maskne Symptoms And Causes: How To Identify Your Type + Editor's Personal Tips For Combating It!
- 5 Skincare Benefits of Facial Cleansing Cream + Popular Hong Kong Product Picks
- Oil-Control Powder Foundations: 6 Best High-Value Picks Loved By Users + Complete Usage Guide
7
Last Few Words


免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

1. Can taking doxycycline for acne lead to a yeast infection, and what should I do if it happens?
Yes, taking doxycycline, like other antibiotics, can sometimes result in a yeast infection due to its effect on the body's natural bacterial balance. If you suspect a yeast infection while on doxycycline treatment, it's important to contact your doctor immediately for appropriate management and treatment.
2. What is the typical doxycycline dosage for treating severe acne, and how long is it usually prescribed?
The doxycycline dosage for acne treatment generally ranges from 50 to 100 mg taken once or twice daily, depending on the severity of the acne and the patient's response to the medication. Treatment duration can vary, but it's often prescribed for several weeks to months. It's crucial to follow your healthcare provider's instructions regarding dosage and duration of treatment.
3. Are topical antibiotics or topical treatments effective in hormonal acne treatment, and how do they compare to oral medications like doxycycline?
Topical antibiotics and other topical treatments can be effective in treating mild to moderate hormonal acne. However, for more severe cases or when topical medications are insufficient, oral medications like doxycycline may be used. The choice of treatment depends on the acne's severity, skin type, and the individual's response to different therapies.
4. When taking doxycycline for acne, can I also use topical medications, and are there any specific combinations to avoid?
Yes, it's common to use topical medications alongside doxycycline to treat acne. Combining oral and topical treatments can enhance the overall effectiveness. However, it's important to consult your healthcare provider about which topical treatments are safe to use with doxycycline, as some combinations might cause skin irritation or other issues.
5. What conditions are commonly used to treat with doxycycline besides acne?
Besides acne, doxycycline is used to treat a variety of bacterial infections, including respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, certain types of sexually transmitted infections, and some forms of Lyme disease. It's also used for malaria prophylaxis in certain situations. As with any medication, it should only be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.