- Home
- Trend
- Weight Loss Strategies
- Acne Tips
- Hair Health Information
- Blemish Removal Tips
- Acne Scar Removal Tips
- Muscle Building Techniques
- Intimate Care Tips
- Postpartum Intimate Care
- Eye Bags Wiki
- Tips for Face Slimming
- Secret of Permanent Hair Removal
- Breast Enlargement Tips
- Cure to Snoring
- Marionette Lines
- Skin-Tightening Secrets
What should you do when your skin itches unbearably? Many people with unstable skin experience itching in multiple areas—face, hands, legs, and areas covered by clothing. But what exactly causes this persistent discomfort? It’s closely linked to skin cell function, hormonal balance, and environmental factors.
Here, we provide an in-depth analysis of 9 major causes of skin itch along with comprehensive treatment methods recommended by nutritionists and medical professionals, guaranteed to refresh your knowledge on skin health!
Why Is My Skin So Itchy? 9 Common Causes of Skin Itch
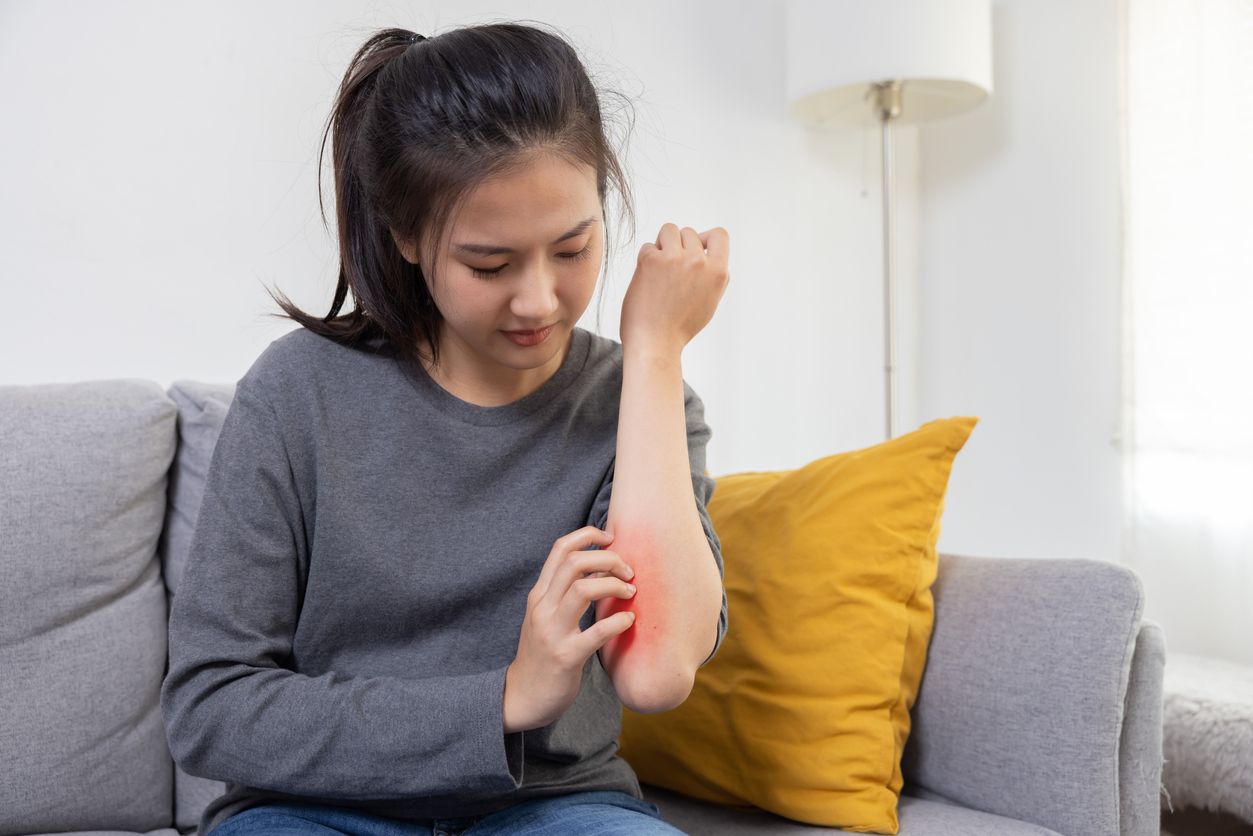

1. Weather Changes: Dryness & Temperature Shifts Damage the Skin Barrier
Changes in climate are a common external factor causing itchy skin. During autumn and winter, dry air and low humidity can leave skin dehydrated and itchy. In hot weather, sweat contains salts that may irritate the skin. Sudden temperature fluctuations affect blood vessel expansion and contraction, overstimulating nerve endings and triggering itchiness.
2. Chronic Skin Conditions: Eczema, Psoriasis, and Recurring Irritation
Chronic skin conditions such as eczema, atopic dermatitis, and psoriasis are major causes of long-term itching. They often come with dryness, rashes, or flaking. Environmental factors, emotional stress, and immune system status influence flare-ups. Continuous itching disrupts sleep and quality of life, creating a “scratch—more itch—scratch” cycle.
3. Acute Allergic Reactions: Sudden Intense Itch
Contact with allergens—foods, medications, cosmetics, pollen, or animal hair—can trigger acute allergic reactions like hives or drug rashes, causing sudden redness, swelling, and severe itching. These reactions appear within minutes to hours and require prompt identification of the allergen to prevent systemic reactions.
4. Nervous & Immune System Disorders: Internal Sources of Itch
Itchiness may not always originate from skin irritation but from abnormal nervous or immune system function. Conditions like neurodermatitis, multiple sclerosis, or post-shingles neuralgia can cause itch without obvious skin lesions. Overactive or dysregulated immunity (autoimmune diseases, HIV) can also disrupt the skin barrier, leading to chronic itching.
5. Hormonal Changes: Adolescence, Pregnancy, or Menopause
Hormonal fluctuations affect skin sensitivity and condition. During adolescence, increased sebum can block follicles and cause inflammation, leading to itch. Pregnancy-related hormone shifts may trigger pruritus gravidarum, while menopausal estrogen decline can leave skin dry, fragile, and persistently itchy.
6. Drug Allergies & Side Effects: Unintended Reactions
Some medications—antibiotics, painkillers, or antihypertensives—can cause drug-induced rashes, purpura, or itchy swelling. Certain drugs may also interfere with nerve signaling or sebum metabolism, leading to unexplained itchiness. Monitoring reactions after taking new medications is essential.
7. Insect Bites: Local Inflammation Triggering Itch
Mosquitoes, fleas, mites, and bedbugs inject saliva or toxins, causing local immune reactions with redness, bumps, and intense itching. Some people are highly sensitive, experiencing blisters or severe allergic responses, particularly in humid environments. Proper personal and home protection is key.
8. Lifestyle & Stress Accumulation: Mind-Body Effects on Skin
Poor habits like late nights, greasy diets, or lack of exercise affect metabolism and hormonal balance, making skin more sensitive or inflamed. Chronic stress elevates cortisol, interfering with immune regulation and the skin barrier, leading to dryness, itchiness, or allergies. Stress-related itch is increasingly common and requires both lifestyle and psychological adjustments.
9. Poor Hygiene Habits: Dust Mites & Hidden Allergens
Inadequate cleaning or poor environmental hygiene can contribute to itching. Failing to change bed linens or pillowcases encourages dust mites, whose droppings and debris are known allergens. Excessive or harsh bathing can also damage the skin barrier, causing dryness and itchiness.
6 Common Symptoms of Skin Itch: When to See a Doctor
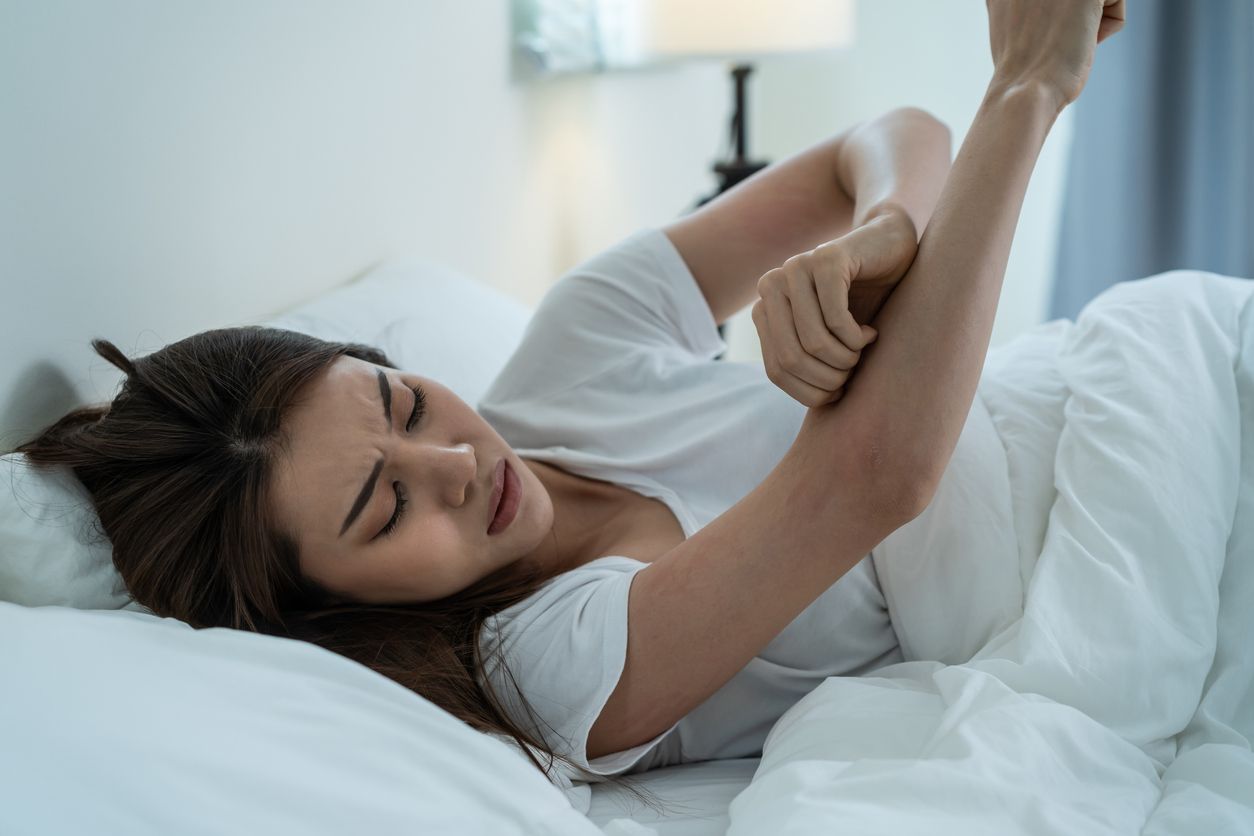

Symptoms vary depending on the cause of itchiness. Recognizing them helps you detect problems early and take appropriate action:
• Persistent Itch: Continuous or intermittent itching is the main symptom.
• Redness & Swelling: Skin may appear red or inflamed.
• Rashes: Various forms of rashes may develop, including bumps or blisters.
• Dryness & Peeling: Skin may become dry, flake, or crack.
• Skin Thickening/Lichenification: Long-term scratching can thicken and roughen skin.
• Scratch Marks: Marks from scratching may cause skin damage or infection.
Other Signs: Seek medical attention if itching is prolonged, severe, disrupts sleep or daily life, or is accompanied by fever, swollen lymph nodes, or other systemic symptoms.
免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
4 Effective Treatments for Skin Itch: Is Vitamin A Important?
1. Anti-Itch Topical Treatments
• Steroid Creams: Anti-inflammatory and anti-itch, but long-term use may cause side effects.
• Antihistamine Creams: Relieve allergy-induced itch.
• Moisturizing Ointments: Ideal for dryness-related itch.
• Oral Medications: Vitamin A, isotretinoin, antihistamines, or steroids.
• Note: Always use under medical supervision.
2. Phototherapy
UVB therapy treats itch caused by conditions like eczema or psoriasis. Can be administered via home devices or professional clinic sessions.
3. Wet Dressings
Effective for dry or inflamed skin-induced itch. Provides temporary relief but may not resolve underlying causes.
4. Lifestyle Adjustments
• Avoid contact with irritants or allergens.
• Wear loose, breathable clothing.
• Keep surroundings cool and use humidifiers to maintain skin moisture.
Prevention Is Better Than Cure: Must-Know Tips to Avoid Skin Itch
Daily habits can prevent itchiness:
• Cleanse & Moisturize: Use gentle cleansers; apply moisturizer after bathing.
• Avoid Allergens: Identify and stay away from known triggers.
• Wear Comfortable Clothing: Choose cotton and breathable fabrics.
• Maintain a Cool Environment: Use fans or air conditioning and ensure ventilation.
• Manage Stress: Practice stress management and relaxation techniques.
• Diet Considerations: Limit spicy or irritating foods.
• Use Gentle Cleansers: Avoid products with alcohol or fragrance.
Ultimate Solution for Skin Itch: Perfect Medical Acne Treatment
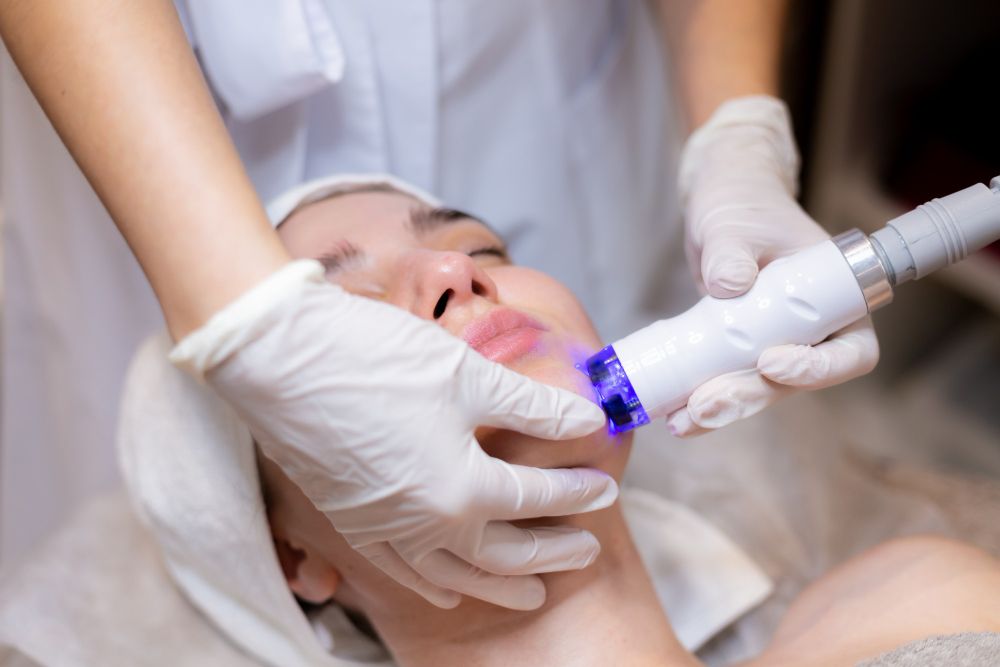
Can’t find the cause of your itch? You might not need complex treatments! Try the pain-free, non-invasive Perfect Medical Acne Treatment. It helps relieve and improve a wide range of skin issues, including rashes, acne, post-acne marks, blackheads, whiteheads, uneven texture, large pores, dehydration, and dullness.
The treatment uses advanced dual-spiral suction + vacuum microdermabrasion, offering deep cleansing while balancing skin hydration and oil. It gently softens old keratin, clears clogged follicles, and stimulates collagen production from the skin base. This ensures that suboptimal skin problems like persistent itchiness are significantly improved and less likely to recur. Book your trial today: Professional Skin Analysis + Perfect Medical Acne Treatment
免費體驗
Acne Treatment
1 Minute Self-Registration
Date should not be before minimal date
FAQ

1. Is skin itch a sign of cellulitis?
Possibly. Cellulitis may not always cause itch but typically shows localized redness, swelling, and pain. Diagnosis requires professional evaluation.
2. How is skin itch related to the liver?
Inflammation or tumors in the liver, gallbladder, or pancreas can block bile flow. Bile accumulation in the skin may cause itch, sometimes signaling increased risk of pancreatic issues.
3. Can weather changes be the main cause of skin itch?
Yes. Environmental changes can trigger itch during skin adaptation. Sunburn-induced itching is a common example.
4. Can chemical exposure cause skin itch?
Yes. Allergic reactions to chemicals—through contact or absorption—can trigger itchiness.
5. What is folliculitis?
A common itchy skin condition, mainly affecting the scalp but can also occur on the face, often causing pimples or acne-like inflammation.